India’s EV Revolution: Scaling 3-Wheeled Commercial Transport [2025 Update]
Raghav Bharadwaj
Chief Executive Officer
Published on:
24 Jul, 2023
Updated on:
24 Dec, 2025
![India’s EV Revolution: Scaling 3-Wheeled Commercial Transport [2025 Update]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fbolt-wordpress.bolt.earth%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F3_wheeled_Commercial_Transport_Feature_Image_163771ee6b.jpg&w=2048&q=75&dpl=3352affa-fe16-4c52-9ede-4130f39ac54c)
India’s bustling cities are undergoing a major transport transformation, with electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles.
Commonly referred to as electric rickshaws or e-rickshaws, these vehicles are steadily gaining traction in India’s bustling urban landscape. Their economic and eco-friendly nature positions them as a pivotal component in India’s stride towards 2030 EV adoption targets.
In this article, we will take a deep dive into the 3-wheeler scene in India, focusing specifically on these three questions:
- What is the current state of electric commercial transport vehicles and 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles in India?
- How can India resolve the challenges preventing 3-wheelers from scaling up?
- Why should key players enable the transition to electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles in India?
Current Status of 3-Wheeled Commercial Transport Vehicles
In India’s transportation system, 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles, notably auto-rickshaws, hold a key place, often bridging the crucial last mile of a commute. Despite their usefulness, traditional auto-rickshaws, which run on internal combustion engines (ICE), are significant contributors to urban air pollution.
On the other hand, the introduction of electric rickshaws (e-rickshaws), which produce no tailpipe emissions and operate quietly, promises to address both mobility needs and environmental concerns.
As of 2025, electric 3-wheelers account for nearly 85% of India’s EV sales, clearly showing their dominance in the EV market.
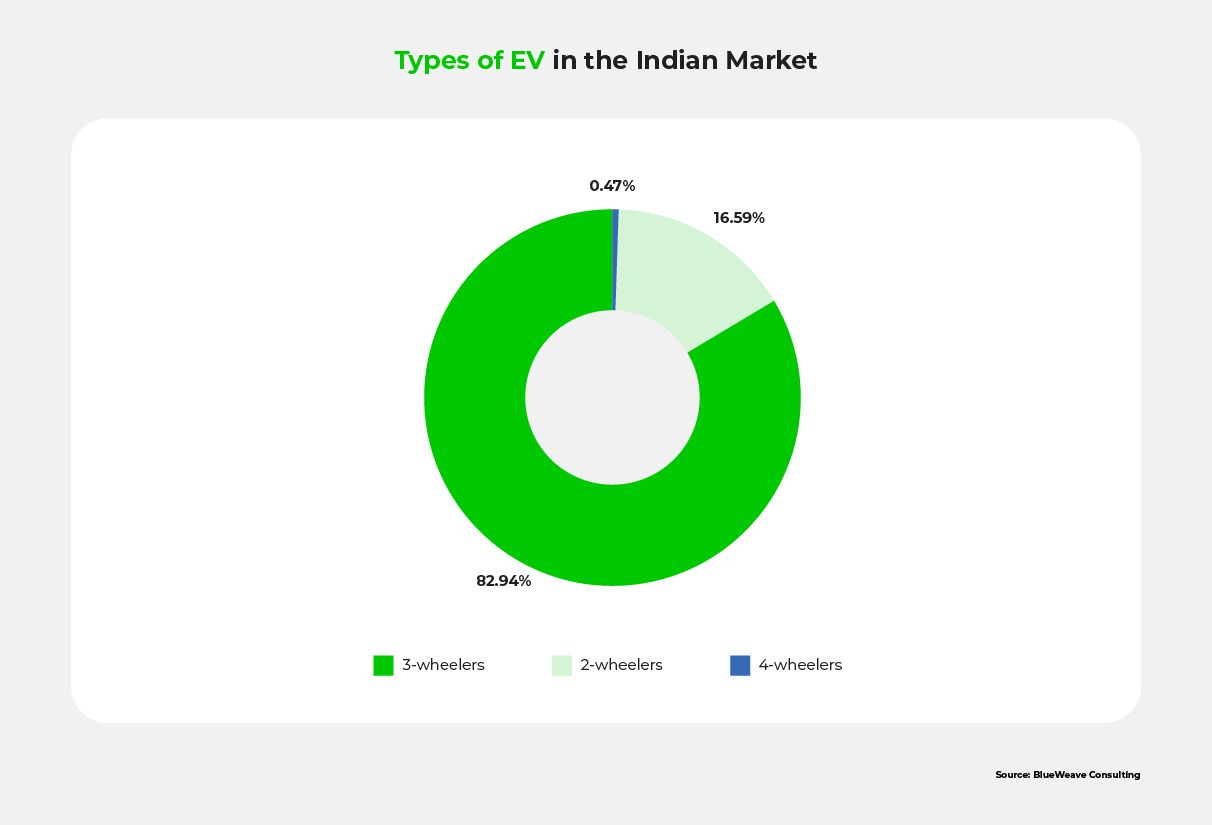
However, powering up this growing number of vehicles will require an extensive charging infrastructure. The good news is India has crossed 3,200 public EV charging stations nationwide, surpassing its earlier 2025 target of 2,600. India aims for 80% electrification of 2- and 3-wheelers by 2030.
Currently, the charging infrastructure in India extends to homes and workplaces. It also offers both fast and slow charging solutions. Although this range of options accommodates different charging needs, it may not be enough to support the country-wide shift to EVs.
Achieving a sustainable EV charging infrastructure will be key to powering the commercial 3-wheeler sector in India. However, this will require private sector investment and a comprehensive shift to renewable energy-supported EV charging. This might prove to be a challenging task for India.
Key Challenges in the Path of India’s EV Infrastructure Growth
Electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles are becoming increasingly popular in India, but the supporting infrastructure is still in its early stages. Unfortunately, the journey to scale up this infrastructure to power up the 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles is fraught with challenges.
Below, we look at four key challenges that are hindering India’s EV infrastructure scale-up.
1. Power Grid Capacity
With rising EV adoption, India’s grid is already under pressure, and the anticipated surge in EVs by 2030 is expected to place significant strain on India’s power grid, potentially leading to power outages, as per a Brookings report. Moreover, uneven electricity access and fluctuating power supply across the country could further complicate the deployment of EVs.
2. Charging Infrastructure Gaps
The current EV-to-charge ratio in India is approximately 120:1, far higher than the global benchmark of 6-20:1.
The charging infrastructure in India also faces another issue: its lack of standardization, which increases costs for operators. However, significant efforts are made by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) to introduce national standards.
Despite its promising future, battery swapping demands substantial upfront investment and presents several operational difficulties. It also raises legal liability concerns involving vehicle manufacturers, swap operators, and drivers in the event of accidents.
3. Technological Developments
Technological advancements are making EVs safer, more convenient, and more accessible. However, the faster the EV industry advances, the harder it becomes to keep abreast of the changes. If the country cannot keep up with the improvements, the EV sector might suffer greatly.
Below, we take a look at some of these technological developments and why India might struggle to implement them:
- Solar charging for electric rickshaws. The current solar panels for e-rickshaws are made using cheap imported materials. But improving these panels for safety and comfort may make the current price skyrocket. This would drive away potential buyers, thus reducing the overall interest in new tech.
- Battery capacity improvements. Electric 3-wheelers typically have a shorter range per charge. But an increase in battery capacity may add to its weight, making 3-wheelers less desirable for users.
- Lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are preferred for their fast charging and superior performance. But India’s limited lithium reserves hinder local battery production, leading to increased imports and higher overall EV costs.
4. Consumer Awareness and Acceptance
Consumer perceptions greatly influence EV adoption. Despite the growing range of electric options, potential buyers often lack awareness about government incentives, the economic benefits of EVs, and advances in EV technology. This knowledge gap can affect their purchasing decisions.
An additional reason why consumers may have less interest in EVs is the lack of charging equipment and infrastructure. Although 50-90% of all EV charging happens at home, charging equipment in India may be unavailable for those without private parking amenities. Lack of charging infrastructure also raises concerns about a 3-wheeler EV’s driving range.
Low awareness of EVs, combined with range anxiety, also puts a damper on India’s overall adoption of electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles.

Strategies for Boosting India’s EV Infrastructure for Commercial Transport
Addressing India’s infrastructure- and consumer-related challenges is key to scaling up the adoption of commercial 3-wheeler EVs. Policymakers and other key players will have to come together to implement innovative strategies that will pave the way for the full adoption of EVs in India.
Below, we highlight four potential solutions that can help address the challenges facing EV 3-wheelers in India.
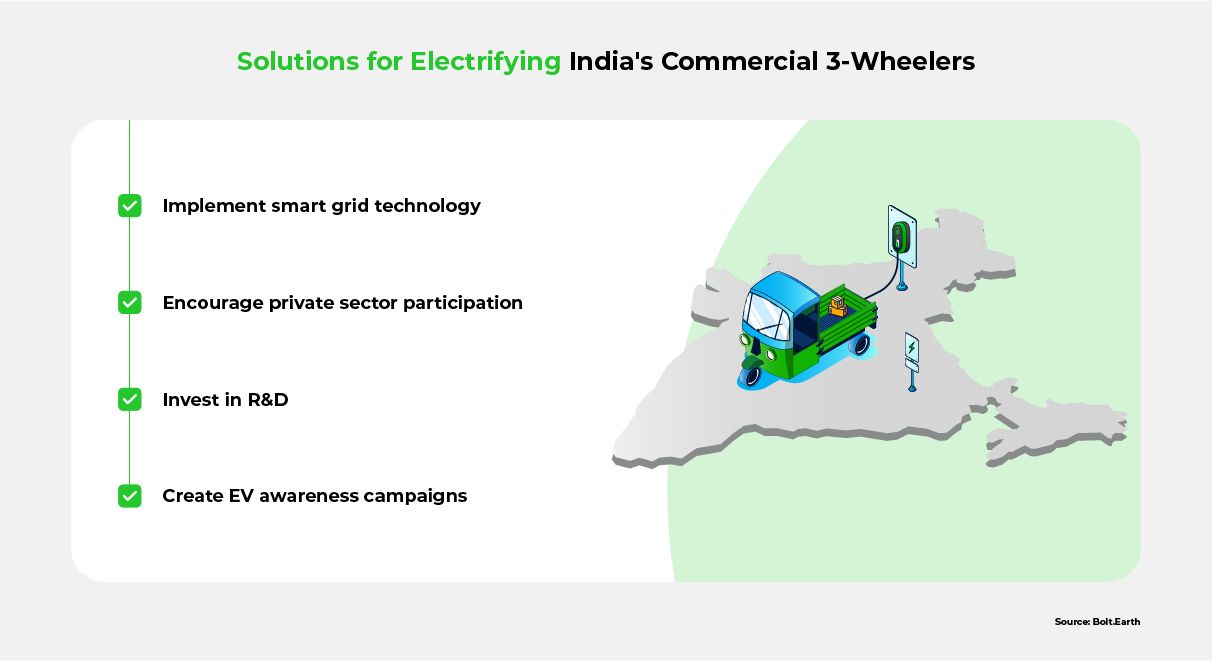
1. Harness Smart Grid Technology
A smart grid, which integrates information and communication technology, offers an upgrade over the conventional grid. It allows two-way transmission of both energy and information, bolstering security, efficiency, and responsiveness.
To implement this smart grid across the country, the Indian government should offer financial support and policy encouragement. Below are some aspects to focus on:
- The three components of a smart grid. It’s crucial to invest in energy storage units, communication systems, data analysis, and management systems for the smart grid.
- Integration of Decentralized Energy Resources and Renewable Energy. These two together can boost India’s energy mix and increase energy storage units.
- Smart meter devices and demand response systems. These systems are key to help monitor the grid and optimize its performance.
A smart grid can help resolve India’s power management issues. It can offer more efficient and reliable electricity distribution, which means it can help the country manage the increased electricity demand from charging.
A smart grid also has diagnostic features that can help reduce power outages and improve EV drivers’ access to electricity. Implementing smart grid technology will be key to helping India support the widespread adoption of 3-wheeler EVs.
2. Promote Private Sector Investment
Investments from the private sector are pivotal in facilitating the transition towards sustainable transportation. Investment in charging infrastructure will especially be helpful to support the growing number of 3-wheeler EVs on the road. To this end, India can propose a 5-dimensional plan:
- Provide tax incentives and streamlined approval processes to attract private investments
- Introduce PPP models to combine government support and private expertise
- Improve charging infrastructure and deploy advanced technologies
- Drive demand by boosting public awareness
- Encourage EV financing to provide accessible and competitive EVs
India can learn from countries like the US and China, which have greatly benefited from private sector investments. Private sector investment can help India address its infrastructure challenges. And coupled with a nationwide EV policy, charging infrastructure can make the commercial 3-wheeler EV sector a success.
3. Invest in R&D
Funding for research and development is vital to propel advancements in EV technology, leading to more efficient electric 3-wheelers. R&D can help India better understand the hurdles standing in the way of technological advancement. It can also shed light on solutions to those problems.
Below are some suggestions to help India promote investment in R&D:
- Allocate a larger budget for R&D
- Encourage public-private partnerships
- Promote venture capital and private equity investments
- Engage in international collaborations
- Establish dedicated research grants
- Encourage industry contributions
These measures will help attract funding, drive innovation, and accelerate advancements in electric vehicle technologies. As a result, EV technology will continue to improve and become safer, more convenient, and more accessible for all. This will greatly promote the demand for EVs, especially for electric 3-wheeler commercial transport vehicles.
4. Create EV Awareness Campaigns
Given the limited vehicle deployment and lack of exposure to charging stations, consumer awareness about EVs in India is still relatively low. Addressing this requires concerted awareness campaigns to educate consumers about EV purchasing, subsidies, performance, and charging station locations.
- Propose campaigns at different political levels
- Involve more participants, like private sector players and educational institutions
- Leverage social media and press platforms
These campaigns are a very effective way to broadcast the benefits of EVs. For example, in 2021, India launched the “GO Electric” Campaign to raise awareness and instill confidence among EV manufacturers and consumers. The campaign included workshops, webinars, technical talks, seminars, and road shows to connect with the masses and promote the adoption of electric vehicles. Creating similar campaigns can help more people know about the benefits of EVs, making them more desirable.
The Role of Government Incentives & Public-Private Partnerships
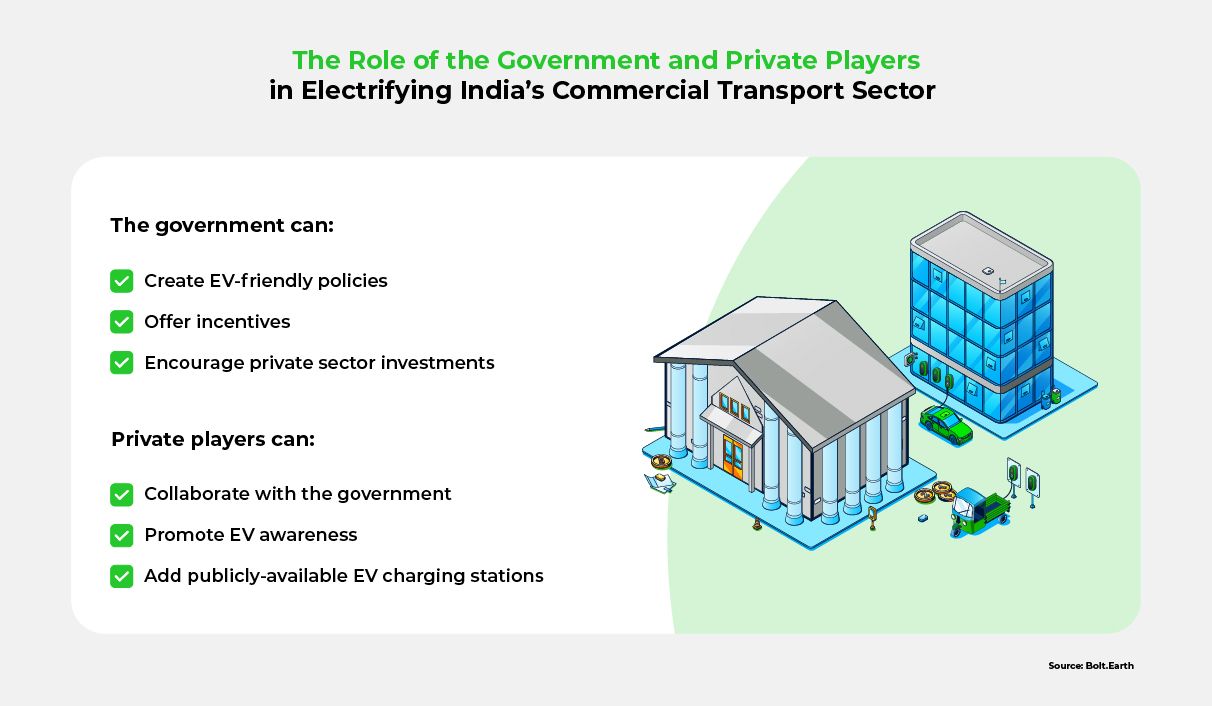
The successful deployment of electric vehicles is contingent on robust and reliable charging infrastructure. Additionally, policy frameworks that are tailored to local circumstances can greatly assist this rollout. Both government policies and public-private partnerships can be instrumental in facilitating the transition to electric 3-wheelers.
Although India has already rolled out 18 state-level policies, all focus almost exclusively on infrastructure development. While this can help address India’s needs for EV charging, it falls short of resolving the other significant obstacles in the electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicle ecosystem.
Below, we take a look at other countries’ examples and how they created policies to improve the state of their EV ecosystems. India can then take inspiration from these countries and create more comprehensive policies and partnerships that can fully cover the challenges it faces.
International Best Practices in Government Policies
International experience has shown that policymakers at all levels, from local to international authorities, play a crucial role in deploying public charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. Their intervention is necessary to address range anxiety and ensure sufficient coverage beyond highways and major cities.
International government policies can help address many of the primary challenges faced by India’s 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicle sector. Here are some examples:
Policies to Address Grid Issues
- France declared that a portion of public EV connection costs may be assumed by the grid operator.
- California’s Public Utilities Commission mandates that utilities provide “utility-side make-ready” infrastructure to support EV charging.
Policies to Address Infrastructure Challenges
- Portugal established a network management body to deploy public charging infrastructure and ensure interoperability and scalability.
- Korea implemented a Smart Energy Strategy to ensure open access to all charging stations with a single membership card.
- Indonesia detailed requirements for EV charging stations and battery swap stations, and offered tax breaks for the deployment of charging infrastructure.
Policies to Promote Technological Advances
- The Netherlands created a public-private platform to research, implement, and inform about EV policies
Policies to Raise Awareness and Acceptance of EVs
- China supports local governments with financial assistance for EV equipment roll-out if they have met their EV adoption targets.
- Chile created the “Mi Taxi Electrico” program to encourage public transportation to switch from ICE to EV.
Successful Public-Private Partnerships in Other Countries
In China, the government and utility companies heavily invest in EV charging infrastructure, supplemented by private investments. PPP initiatives in China merge public and social capital to drive the implementation of a nationwide EV charging infrastructure.
Policies, incentives, and programs guide this development, while automakers and energy companies enhance charging infrastructure through acquisitions and joint ventures.
In the US, a mix of federal and state programs, utility investments, private funding, and scandal settlement proceeds has facilitated the growth of the EV charging network. Despite the need for more public-private partnerships, the US is now home to 130,000+ public charging stations, minus private slow chargers.
Strategies for Effective Public-Private Partnerships in India
Despite the differences between these countries, China and the US’s success stories can be inspiring for India. Leveraging lessons from them can help India adopt an ambitious policy approach, which can include:
- Integrating charging infrastructure investments into utility reforms
- Optimizing charger utilization through strategic siting
- Providing financing options, like low-interest loans
- Implementing building codes to make for more EV-ready sites and buildings
Additionally, India should establish clear guidelines and coordinate its efforts to effectively deploy charging stations. Through public-private partnerships, India can, for example:
- Encourage oil companies to establish EV chargers to diversify their portfolio, which also boosts infrastructure development
- Engage non-profit organizations and utilities to promote consumer awareness about EVs, which can also increase EV adoption rates in India
These measures don’t specifically apply to the electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicle sector. They can, however, help India develop a more comprehensive EV charging infrastructure.
By implementing the solutions to combat logistical and consumer-related obstacles, India can pave the way for the full adoption of electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles. The electrification of the transport sector will yield beneficial results for the whole country and its population.
The Impact of an Electric Transportation Sector
Transitioning to electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles in India holds the promise of considerable environmental and economic benefits, aligning with the nation’s transport objectives. Here’s how this transition supports these objectives:
- Environment and air quality: Unlike their traditional counterparts, e-rickshaws produce no tailpipe emissions. This means they can reduce air pollution and improve public health.
- Energy efficiency: Electric vehicles are far more energy-efficient than gasoline-fueled vehicles. As a result, they offer lower operating costs for drivers and contribute to nationwide energy conservation.
- Renewable energy promotion: The surge in e-rickshaw adoption will also increase the need for renewable energy sources like wind and solar power is projected to follow suit. This has the potential to accelerate the growth of India’s renewable energy infrastructure.
- Economic impacts: The growing e-rickshaw market could catalyze job creation in manufacturing, services, and infrastructure sectors. In addition, lower operating costs can boost drivers’ income, stimulating economic growth and potentially alleviating poverty.
- Fulfilling international commitments: The transition to e-rickshaws supports international agreements like the Paris Agreement. This will then help India meet its commitments to combat climate change.
Future Prospects for 3-Wheeler EVs in India
The wider adoption of electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles can offer substantial benefits to India in terms of the environment, public health, and economy.
However, numerous challenges remain that require attention. India still suffers from a weak grid and lacks a robust charging infrastructure. The country is also unable to keep up with progress in EV technology, which also affects consumer perceptions of EVs.
That being said, India should strive to adopt a collaborative approach involving various stakeholders. This will be key to overcoming these challenges. Policies promoting EV adoption, attractive incentives, and renewable energy investments are crucial for this transition.
By fully embracing electric vehicles, India can pave the way for a cleaner, more efficient transportation system, securing a sustainable future for upcoming generations.
To learn more about electric 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles EVs in India, please see the FAQ and Resources sections below.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current status of India’s EV infrastructure for 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles?
India’s EV infrastructure for 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles is still developing. Currently, obstacles such as a lack of charging stations, limited battery swapping facilities, and non-standardized chargers are apparent. However, efforts are in motion to overcome these hurdles, aiming to expand the EV infrastructure and pave the way for a smoother transition to electric vehicles.
How can government policies and private sector investments facilitate the electrification of 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles in India?
Government policies and incentives can encourage private sector investment in the electrification of 3-wheeled commercial transport vehicles in India. These policies can promote manufacturing, charging infrastructure, and technological research for EVs. Public-private partnerships can further accelerate investment and cooperation, fostering an ecosystem that supports the transition to electric vehicles.
What are the benefits of transitioning to EVs in India’s transportation sector?
A move towards electric vehicles within India’s transport system holds the potential to significantly enhance air quality through reduced carbon emissions, increase energy efficiency, and promote economic expansion. In addition, the adoption of EVs can boost the demand for renewable energy sources, lead to job creation, and align India’s commitments to global climate change mitigation efforts.
How could EV adoption impact the commercial transport sector in India?
EV adoption could transform India’s commercial transport sector, leading to cleaner air and better public health due to reduced carbon emissions. Additionally, it could stimulate job growth in manufacturing, service, and infrastructure sectors and contribute to the nation’s overall energy efficiency. It can also support India in meeting its EV adoption targets.


Mar 05, 2026 • EV Charging Infrastructure
The Hidden Cost of Poor Electrical Design in EV Charging Networks
Read More


