How The EV Ecosystem Can Drive EV Adoption in India
Raghav Bharadwaj
Chief Executive Officer
Published on:
24 May, 2023
Updated on:
24 Nov, 2025

India is standing at a crucial crossroads in its journey towards sustainable development. As one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing economies, the country faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility.
To overcome this challenge, India has set ambitious goals for EV penetration as EV adoption has emerged globally. However, with only 1.32% of India’s registered vehicles being EVs in FY 2021-22, the path to achieving the announced target of 30% EVs by 2030 requires a collaborative effort from the government, private sector, and consumers alike.
Embracing an ecosystem approach — where all stakeholders actively participate and contribute — is key to creating a supportive and conducive framework for the growth of India’s EV market. By examining the intricacies of this approach, we can uncover the driving forces behind India’s EV revolution and explore its potential for shaping India’s sustainable future.
This article analyzes the EV ecosystem in India and answers three essential questions:
- What is the current state of EV adoption in India, and why does it need to improve?
- Why is driving EV adoption in India challenging, and how can an EV ecosystem help address these challenges?
- Who are the key players in the Indian EV ecosystem, and how can they work together to electrify India?
The Current State of EV Adoption in India
India’s current EV ecosystem reflects both opportunities and challenges as the nation strives to accelerate EV adoption. While major Indian and international automobile manufacturers such as Hyundai, Kia, and Mercedes-Benz offer a wide range of EV 4-wheeler models, a significant portion of India’s vehicle market comprises 2- and 3-wheelers, which account for about 80% of total vehicle sales.
Surprisingly, out of the 250 million 2- and 3-wheelers on the roads in India, only one million are electric. Nonetheless, in FY 2022-23 alone, India witnessed a surge in EV registrations exceeding one million with electric two-wheelers making up 62% of EVs sold.
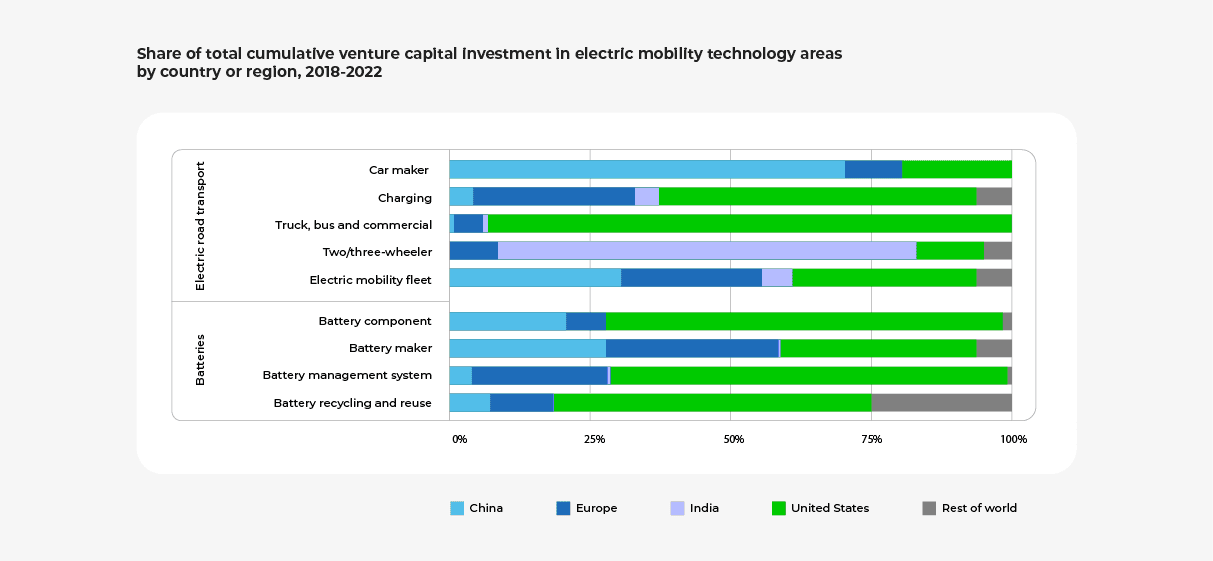
Projections for EV Adoption in India
Ev adoption in India looks promising as its EV market is expected to grow rapidly. By 2030, it’s estimated that 10 million EVs will be sold annually, with a compound annual growth rate of 49% in the coming years.
States that have proactively provided policy and infrastructure support to accelerate this transition are already witnessing sharp increases in EV sales — in December 2022, Delhi reported 16.8% of all vehicle sales were EVs, showcasing an impressive 86% YoY growth.
Present government policies support achieving India’s goal of 30% EVs by 2030. In the 2023-24 budget, a substantial amount of INR 35,000 crore has been allocated for crucial capital investments to facilitate the transition to net-zero energy targets.
Additionally, the allocation for the FAME-II scheme has been increased by 80%, providing subsidies and promotions to encourage EV adoption. These initiatives demonstrate the government’s commitment to creating a sustainable future and promoting the use of EVs in India.
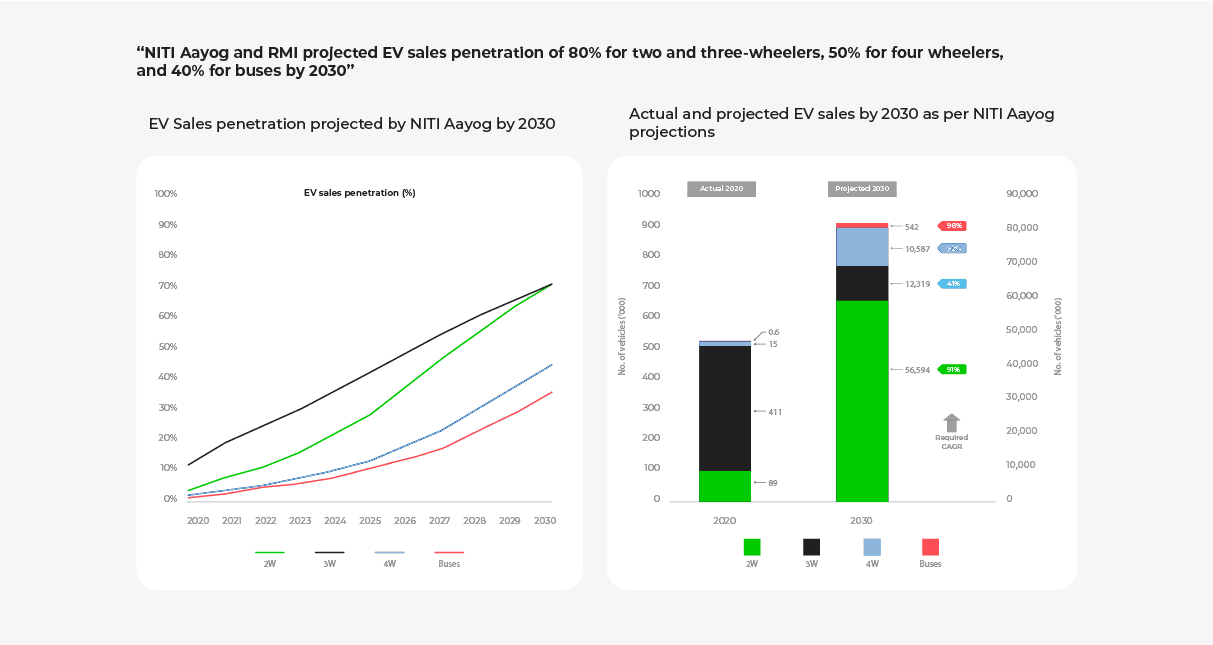
While India is making some progress toward EV adoption, the country still has a pressing need to accelerate adoption and tap into India’s market potential, combat environmental challenges, enhance energy security, and achieve policy objectives.
Below we examine why EV adoption is a necessary step to help India achieve significant economic and environmental benefits
The Need to Drive EV Adoption in India
Environmentally, EVs offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels in the transportation sector as petrol and diesel vehicles emit almost 3x more carbon dioxide than EVs.
Beyond the environmental benefits, widespread adoption holds the potential to transform transportation in India, offering economic advantages like job creation and increased energy security. By reducing emissions and integrating EVs into the transportation framework, a balance between environmental sustainability and economic growth can be struck.
While EV adoption is a very interesting prospect for India, the country is still facing several obstacles preventing it from unlocking the full potential of EVs.
3 Main Challenges to EV Adoption in India
While EVs can reduce emissions and unlock economic benefits, several factors stand in the way of EV adoption in India. Lack of infrastructure, public awareness, and high costs impede progress. Identifying and understanding these challenges is necessary for key players to develop targeted strategies to address them.
1. Lack of Infrastructure
Charging infrastructure requires significant investment in equipment and land, in addition to investments needed to enhance the capacity and efficiency of the power grid.
Without adequate charging infrastructure, consumer demand for electric vehicles will remain severely limited. This will lead to restricted demand for EV charging and investor reluctance to invest in charging infrastructure.
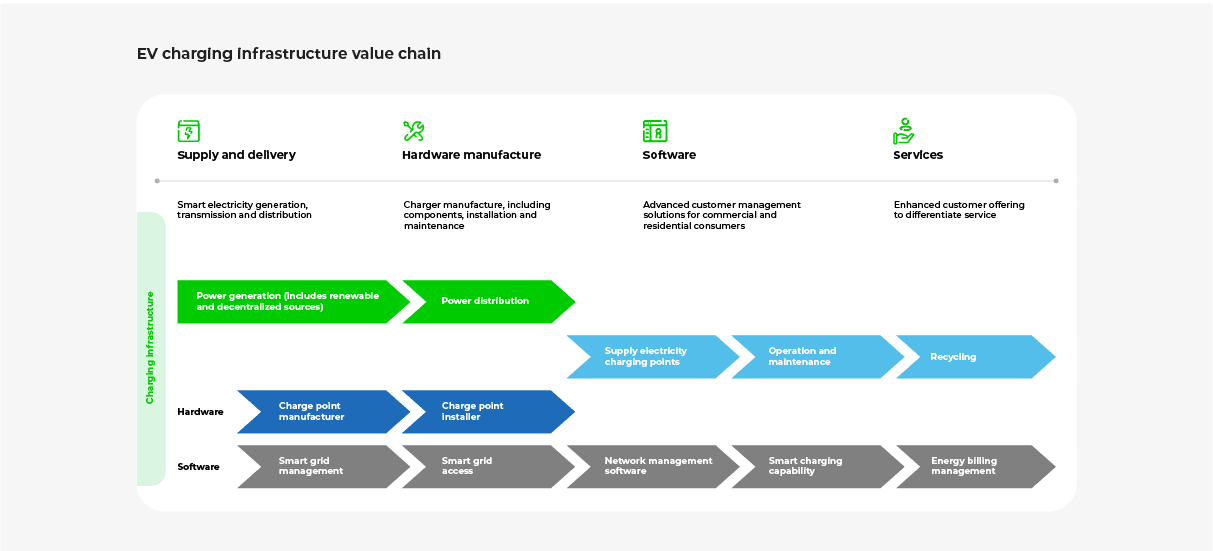
2. High Costs of EVs
The price of an EV is much higher compared to an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle as EVs use battery power instead of fossil fuel. Although EVs have a much simpler design comprising the battery pack, electric motor, and transmission, they are still expensive to produce because of the high cost of the battery.
While lithium-ion technology is the major contributor to EVs’ costs, their batteries also use costly components made up of rare earth metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel — further decreasing the affordability of EVs and driving average consumers away.
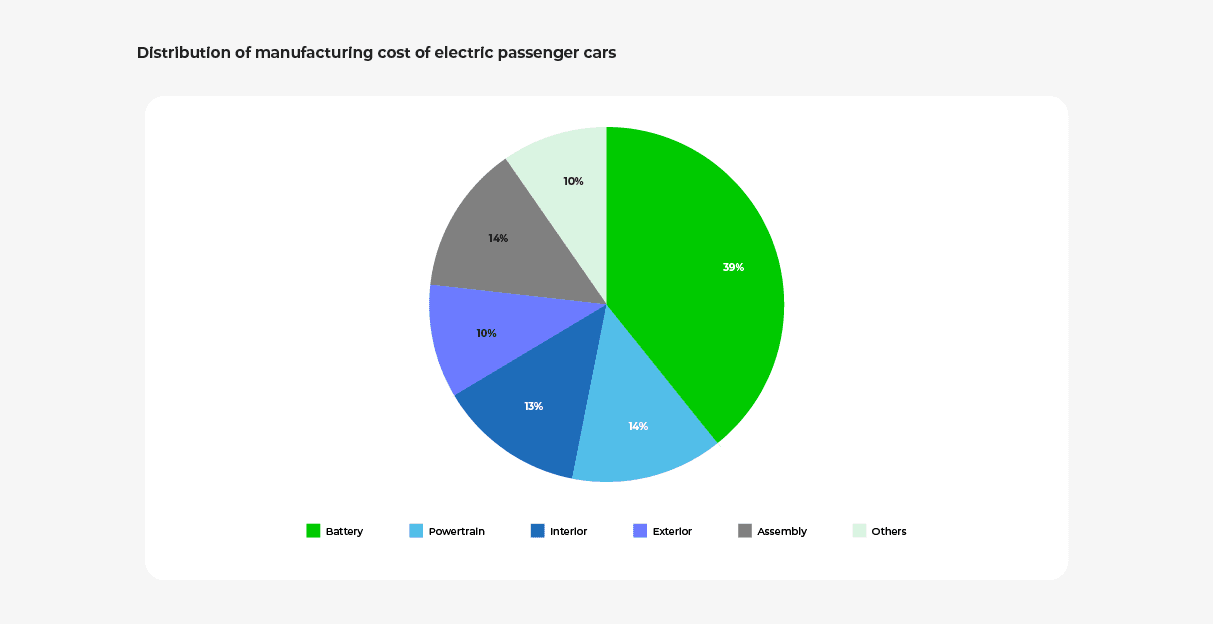
Research and development also contribute to high EV costs. For example, many EV manufacturers are investing in EV software and the vehicle’s operating platform to make EVs more efficient and eventually autonomous.
3. Low Public Awareness
Due to limited outreach and the dominance of traditional vehicles, insufficient information and education leaves many people in India unaware of the benefits of EVs and the role they can play in building a more sustainable future. Consumers may also not be aware of the government’s initiatives and plans to drive EV adoption, making ICE vehicles a go-to choice for lack of external intricacies.
The Ecosystem Strategy to Increase EV Adoption in India
A comprehensive ecosystem approach is key to accelerating EV adoption in India. Different players in the ecosystem can come together to drive infrastructure development, increase the affordability of EVs, and improve public awareness.
Addressing these aspects will allow India to pave the way for a sustainable and widespread transition to e-mobility, fostering a greener and more energy-efficient transportation landscape.
Below, we analyze how an EV ecosystem can help address these challenges, then take a look at the individual players who make up this ecosystem, and what role they play.
1. Infrastructure Development
The Indian government has launched several initiatives to encourage the development of charging infrastructure, such as the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme.
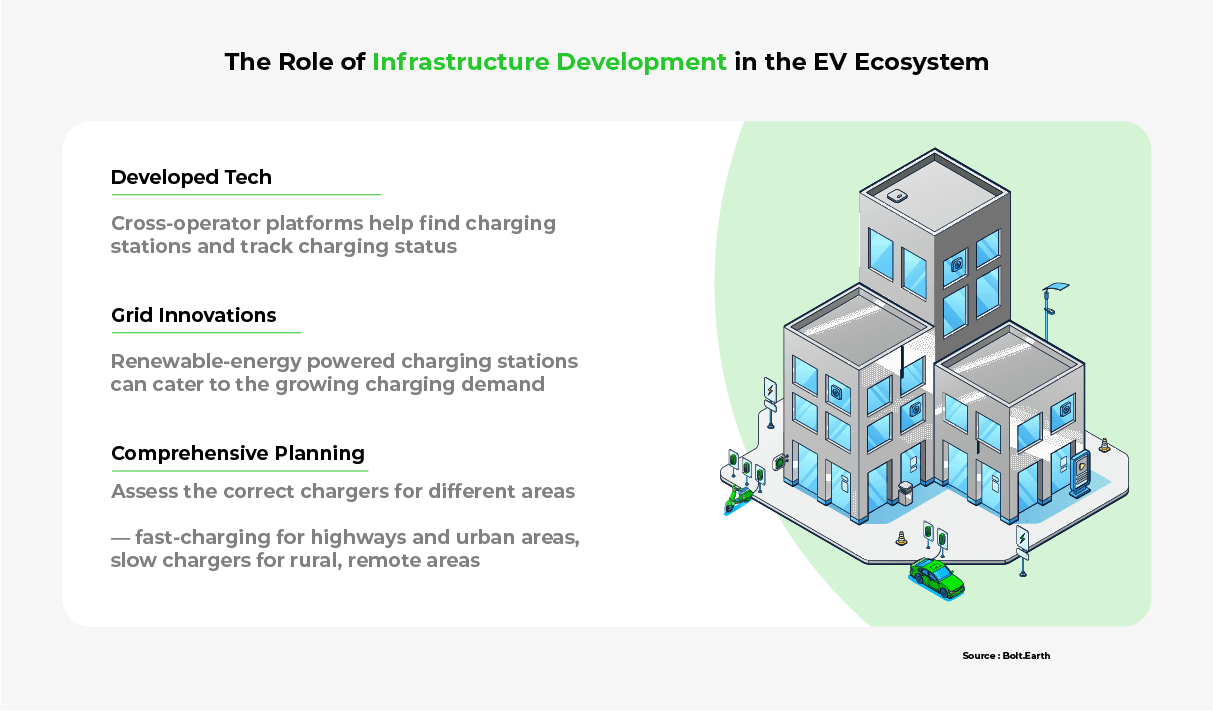
The EV charging ecosystem offers immense potential for innovation. For instance, chargers in parking lots and vertical charging stations. Investment in futuristic solutions such as smart charging systems and battery recycling facilities should also be encouraged. Policymakers should take the lead in bringing together ecosystem players for infrastructure development and guide collaboration among the participants.
To establish an EV ecosystem, policymakers should involve market participants and develop a transparent, holistic roadmap for developing India’s EV Infrastructure. The roadmap to achieve policy goals should emphasize cross-operator synergies, long-term solutions, and comprehensive planning.
2. Improving EV Affordability
The demand for EVs will vary with the price at which it is offered for sale. When the prices are high demand will be low, and when prices drop, demand will go up.
EVs are currently much more expensive than petrol or diesel vehicles in India. Thus, an essential component of the strategy to promote EVs in India is to work towards reducing the price of EVs. For instance, India can encourage greater self-reliance in battery production to reduce dependence on imports like raw material discovery efforts.
Using the ecosystem approach, EV players can develop practical strategies to address concerns about the high cost of EVs in India. Policymakers, for example, can design corporate incentives and consumer subsidies. This will help support local supply and demand, respectively.
3. Awareness Campaigns
Many people are still unfamiliar with the benefits of EV. However, India needs to promote green living among the public. The country should also educate citizens about the benefits of EV adoption. This will encourage more people to switch to EVs.
Awareness campaigns are a vital component in the successful implementation of an EV ecosystem approach. As India navigates this transition, the need to foster awareness for a supportive ecosystem cannot be understated. By educating the public, promoting infrastructure development, and encouraging collaboration, these campaigns create a favorable environment for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
EV manufacturers and charging operators can collaborate with the government to create awareness campaigns. The government can offer incentives and tax breaks to companies that promote EVs. These partnerships can create an integrated campaign to promote EVs, such as the ‘Go Electric’ campaign to encourage the development of an EV ecosystem.
After understanding how an EV ecosystem can help address India’s EV adoption challenges, we can analyze who can take part in this ecosystem — and what they can do.
7 Major Players of the EV Ecosystem in India
Expediting the transition toward widespread EV adoption can’t be an individual effort. Key players have to collaborate and develop practical solutions to tackle the challenges of EV transition.
Below we analyze the roles of seven key players in the EV ecosystem, to see how collaboration among them can make EV transition more affordable, cohesive, efficient, and effective.
1. EV Manufacturers
New and established brands are competing for a share in the EV market. As a result, they are expanding their EVs’ availability and affordability, further driving EV adoption. The Indian consumer now has access to 3-wheelers, cars, buses, and other EV models.
2. Component and Battery Manufacturers
Batteries are one of the most critical components of an EV, and they significantly contribute to an EV’s hefty price tag. Driving EV adoption in India will require component and battery manufacturers to invest in high-performing, cost-effective batteries. Doing so will also help India emerge as a leader in the global EV market.
3. Charging Infrastructure Providers
As range anxiety is one of the key hindrances in EV adoption, charging infrastructure providers can play a critical role in removing this obstacle. By rolling out charging stations across the country, EV drivers can charge their EVs conveniently on the go.
Charging infrastructure providers also have a unique opportunity to leverage software to create interconnected charging networks, with companies leveraging Open Charging Platforms to bring together different providers’ charging points into a single platform.
4. The Government
The Indian government develops policies and regulations that govern the EV industry. Policy support encourages players to invest in the EV ecosystem to develop a competitive EV industry in India and accelerate consumer EV adoption through subsidies and end-user incentives.
5. Investors and Financiers
Investors provide the necessary facilities and infrastructure for the manufacturing, assembly, supply, and servicing of EV components. Consumer financing options from major banks and NBFCs make EVs more affordable and accessible to a wide range of consumers.
6. Consumers
Consumers also have the responsibility to respond to and benefit from other players’ efforts. By taking advantage of subsidies, residential charging infrastructure, and the countless educational resources on EVs, consumers can develop a green mindset, and share it with their peers, further driving the demand for EVs.
7. Other Players
Software pervades many processes in the EV ecosystem, including EV operating systems, charging platforms, and fleet management. Channel partners and dealers educate consumers, promote and market EVs, and provide after-sales services. By introducing technology in every step of the EV adoption process, like single window portals, EV OS apps, etc., EVs can become an even more innovative offering, attracting more consumers.
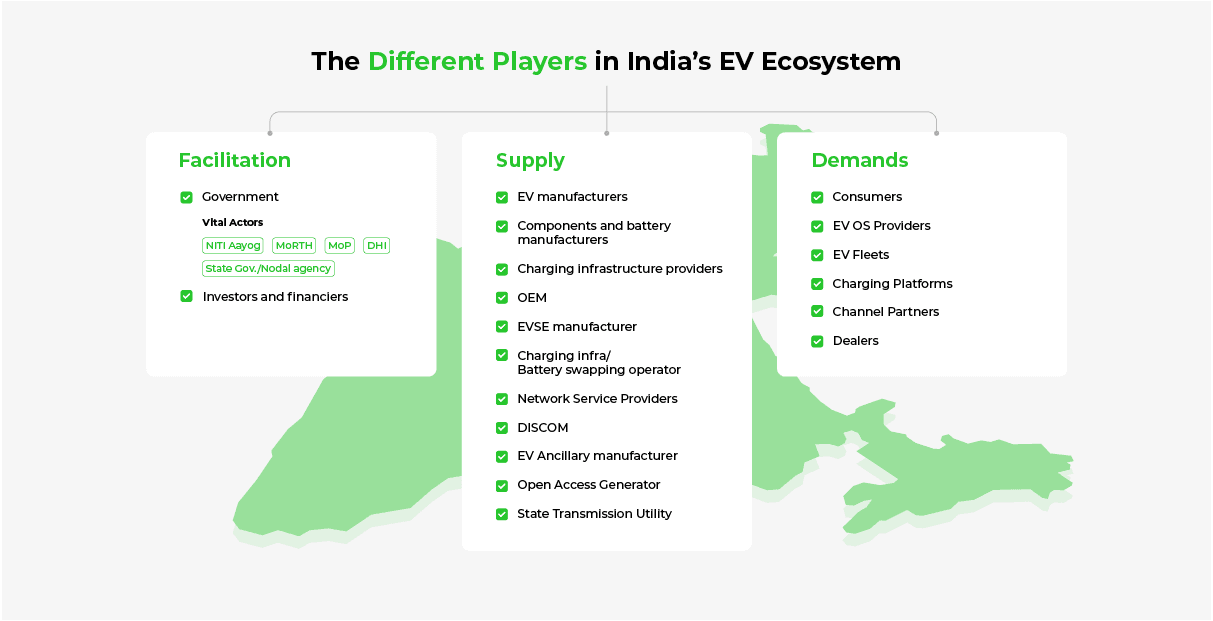
Despite individual players’ efforts, EV adoption requires an interconnected ecosystem. A siloed approach to problem-solving in the EV industry will only hinder the transition to EVs, as each player focuses on their personal views and objectives.
Conversely, all players in the EV industry should set aside their preferences, and focus on the primary goal: driving EV adoption in India; they should trust that putting the country’s needs first will ultimately benefit them and their agendas.
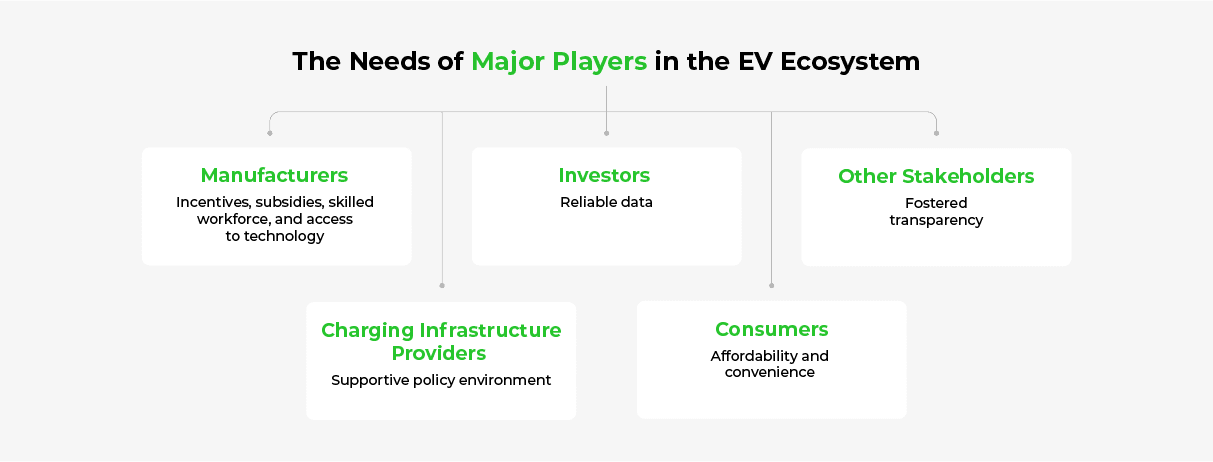
An EV Ecosystem That Fulfills All Players’ Needs
An EV ecosystem presents a unique opportunity to drive the EV revolution in India. This approach can address the many challenges faced by EV adoption by fostering collaboration between key players while boosting the economy and establishing a sustainable future.
It is important to involve the key EV stakeholders in the planning and development of strategies to achieve the targeted EV adoption in India. Policymakers and industry leaders can use the ecosystem approach to effectively bring together all stakeholders, from consumers to manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers.
The players should aim to achieve synergy in the ecosystem so that the action of the players has a multiplier effect through effective collaboration. The transition to EVs will be faster and seamless when the needs of EV players are met efficiently.
To learn more about the EV ecosystem in India, please see the FAQ and Resources sections below.
FAQ
What is the ecosystem approach to EV adoption?
The ecosystem approach aims to bring together all the players in the EV industry to collaborate and work synergistically. EV technology is at a nascent stage and different segments of the industry — EV manufacturers, battery companies, charging providers, and investors — need to establish a shared perspective of the future they are trying to create. Without this, EV players may work with different perspectives in silos and impede progress.
Who are the major players in the Indian EV ecosystem?
The Indian EV ecosystem encompasses all the players who have a role to play in the EV industry in India, including manufacturers, component suppliers, battery companies, dealers, EV charging companies, investors, policymakers, and consumers. Different segments of the EV industry will have their own subset of an ecosystem.
Why do we need to build an EV ecosystem in India?
A comprehensive EV ecosystem offers a sustainable alternative to transportation. EVs will help create a greener future and more robust economy. As per planned policy goal, EV’s contribution to India’s GDP is expected to cross US $150 billion by 2030, and the EV industry will create 10 million new jobs in India by 2030.
How does an EV ecosystem lead to a greener future?
EVs are free from toxic emissions, unlike petrol and diesel vehicles as they have zero tailpipe emissions. EVs can also be charged using renewable energy sources, such as solar power, and can reduce demand for fossil fuels for electricity production.
#### How can businesses and investors benefit from investing in an EV ecosystem?
The Indian EV industry is at a nascent stage. The share of EVs in total vehicle registration is 1.32% despite growing over 130% in the past year. India’s target is to reach 30% EV penetration by 2030. This holds immense potential for players in the EV ecosystem to enable and profit from the EV transition in this decade and beyond.
What are the challenges to driving EV adoption in India?
Building an EV ecosystem in India faces several challenges, like lack of infrastructure, high costs of EVs, and low consumer awareness. Addressing these challenges will require collaboration from different stakeholders in the Indian EV market, and it will be key to boosting adoption in India
How can the challenges of driving EV adoption be overcome?
The challenges to building an EV ecosystem can be overcome through collaborative efforts from all players in the ecosystem. Policymakers should take the lead in bringing together all stakeholders and outlining the roadmap to achieve the policy targets. The needs of the players in the ecosystem need to be identified and fulfilled in a mutually beneficial way through the ecosystem approach.
Resources
International Energy Agency (IEA): Global EV Outlook 2023
Learn how India can catch up with its climate ambitions through EVs.
Arthur D Little: Unlocking India’s Electric Mobility Potential
Understand what can shape the future of EVs in India.
NITI Aayog Report: Analyzing the Status Quo of Different E-Mobility Segments
Read this report to understand the current state of electric mobility and low-carbon transportation in India.
World Economic Forum: Financing India’s Electric 2- and 3-Wheeler Fleets
Read this executive brief from November 2022 to see what strategies can help finance India’s EV fleets.


Mar 05, 2026 • EV Charging Infrastructure
The Hidden Cost of Poor Electrical Design in EV Charging Networks
Read More


