Assessing the Environmental Impact of EVs in India by 2030
Raghav Bharadwaj
Chief Executive Officer
Published on:
06 Jun, 2023
Updated on:
28 Nov, 2025

Transportation is currently a leading cause of air pollution in India. As a result, the government is taking steps to encourage electric vehicle adoption. By embracing EVs, India aims to decarbonize the transportation sector and pave the way for a national transition to clean energy.
Transitioning to EVs promises to reduce air pollution in India’s megacities and provide citizens with better quality of life. This article delves into the projected environmental impact of EVs by 2030 by answering three key questions:
- How does the transportation sector currently impact India’s environment, and what are the expected trends in the coming years?
- How can EV adoption benefit India’s environment?
- Why is it important for every stakeholder to help India balance environmental sustainability with economic development?
India’s Transportation Sector: Current Environmental Challenges
The transportation sector in India has a significant environmental impact. It accounts for around 20% of India’s total energy consumption. Unfortunately, it also contributes to 11% of India’s total carbon dioxide emissions.
This strain on the country’s environment worsens as rapid urbanization and population growth lead to increased traffic congestion, further damaging air quality and increasing fuel consumption. Infrastructure development for transportation requires land acquisition and can result in habitat destruction and ecosystem disruption.
These numbers are only expected to grow as the economy develops and people’s purchasing power increases. Because cars are seen as a status symbol, people’s increasing desire and ability to own one will lead to a surge in pollution.
A recent study estimates that the number of four-wheel vehicles will skyrocket by 900% over the next thirty years, exacerbating the already critical environmental crisis. Additionally, as India’s economy grows, truck emissions will increase, since freight transportation of goods primarily relies on carbon-emitting trucks.
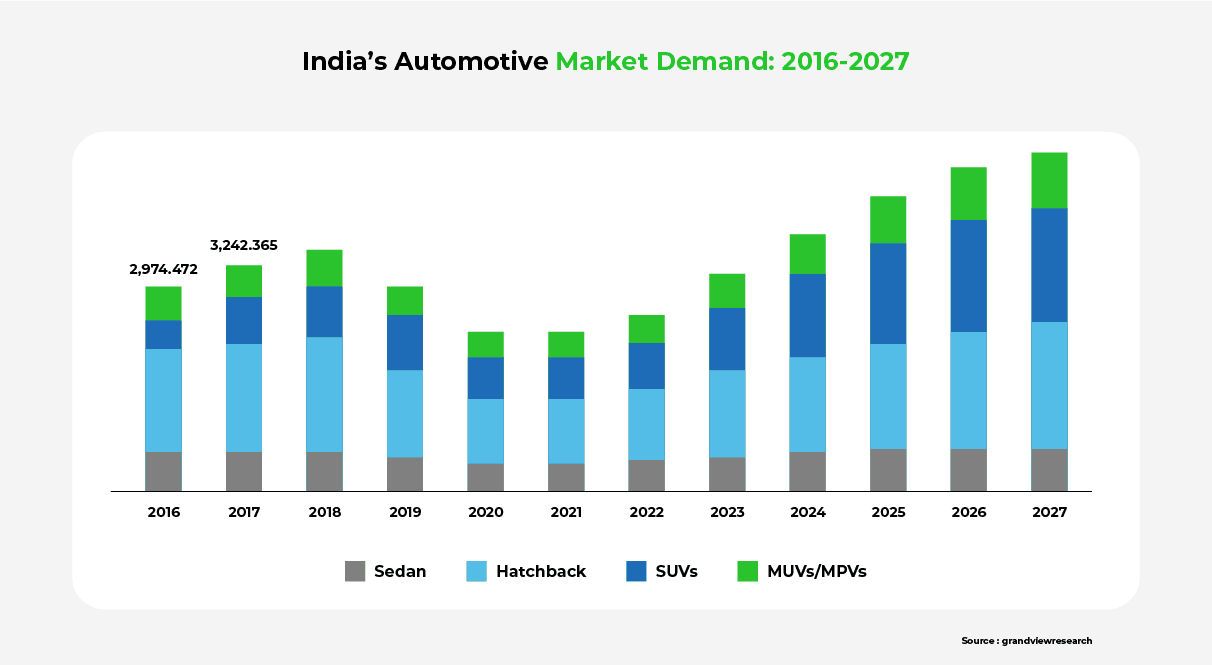
The automotive sector, buoyed by a growing middle class, presents tremendous financial opportunities for investors. Research shows that India received a cumulative FDI equity inflow of $33.77 billion from April 2000 to September 2022. The Indian government expects the automobile sector to attract $8-10 billion in both local and foreign investment in 2023.
While 2023 is expected to be a turning point with increased investments in EVs, the market for traditional ICE vehicles is also expected to grow. This might offset the positive environmental impact of EVs in the coming years.
Key Environmental Challenges from ICE Vehicles
The automotive sector poses several challenges to the environment in India. Current practices for vehicle manufacturing play a role in rapid resource depletion. Once manufactured, these vehicles contribute to greenhouse gas emissions through their dependence on fossil fuels.
This leads to air pollution, adverse health effects, and accelerated climate change, especially in growing urban areas. Examining these barriers and their current impacts on the environment can elucidate the urgent need for sustainable solutions and alternative approaches in the transportation sector.
1. Resource Depletion from Vehicle Manufacturing
Most vehicles are primarily composed of steel, plastic, aluminum, and iron. Mining, manufacturing, and unsustainably utilizing these resources have significant environmental consequences, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and soil degradation.
Another concern is the disposal of traditional vehicles, which often end up in landfills, contributing to waste and pollution. Discarding these vehicles also requires significant energy, further depleting valuable resources.
2. Air Pollution and Public Health Risks
Air pollution is a severe problem in India, with some cities ranking among the most polluted in the world. Out of the many pollutants, vehicular emissions are a top contributor.
The emissions from conventional ICE vehicles contain pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, lead, and benzene. All of these negatively impact human health, as the table below demonstrates.
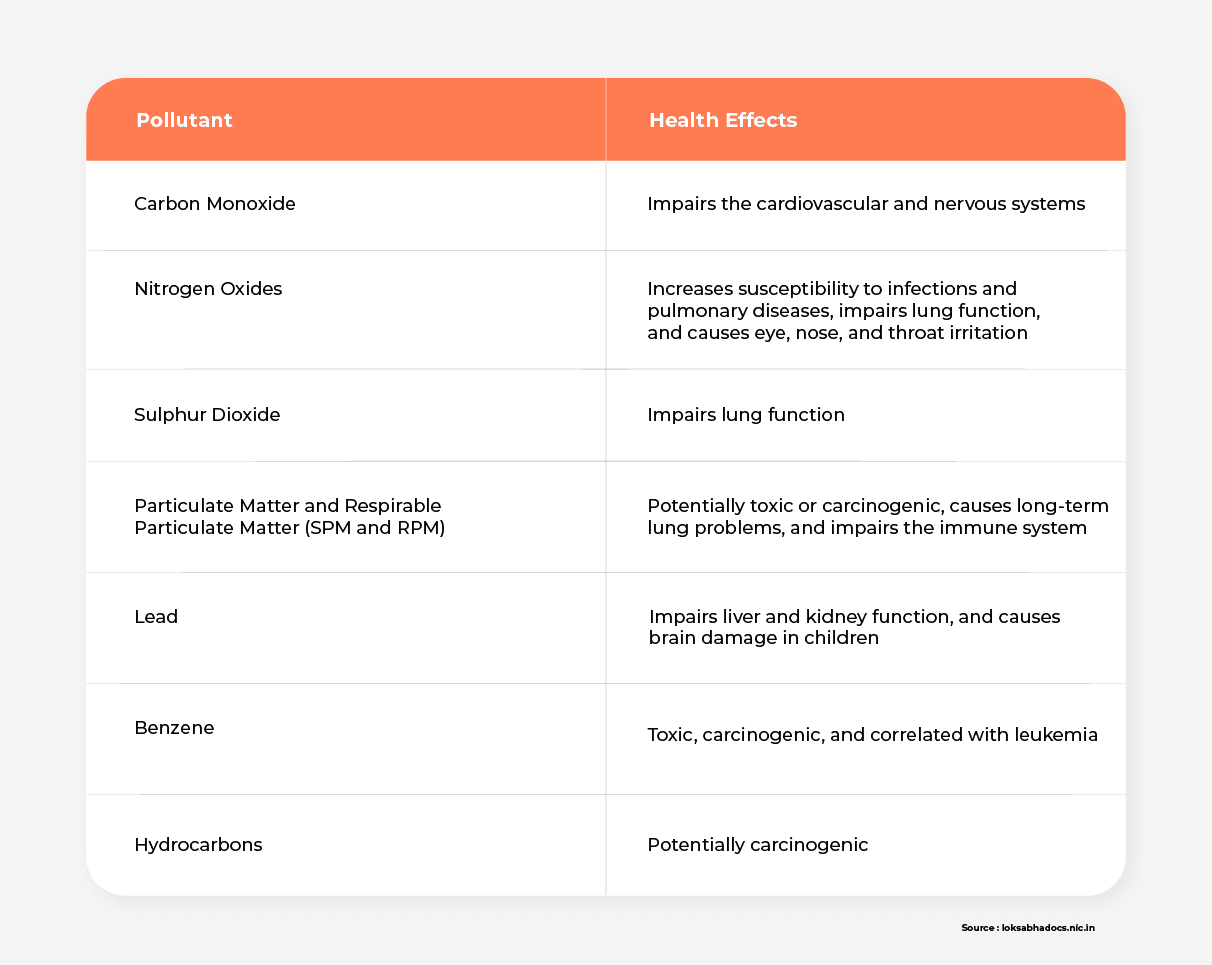
In densely populated urban centers, the concentration of vehicles further exacerbates these health problems. The increasing number of vehicles will raise morbidity and mortality rates among India’s population if this challenge remains unaddressed.
Left unchecked, both resource depletion and air pollution can continue to intensify the greenhouse effect and contribute to ecological disruption.
3. Climate Change and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
India ranks as the third-largest greenhouse gas emitter in the world. The transportation sector significantly contributes to these emissions, with vehicular pollution causing high levels of carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide in particularly congested cities like New Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru. The transportation sector is also responsible for a third of India’s particulate matter pollution, which traps heat and further drives climate change.
The resulting rise in temperatures has adverse effects on public health, including an increase in vector-borne diseases; warmer weather creates favorable conditions for pathogen-bearing organisms, such as mosquitoes, to thrive and breed.
Greenhouse gasses also impact weather patterns, causing droughts, heat waves, and floods, all of which undermine agricultural productivity and increase the risk of food insecurity.
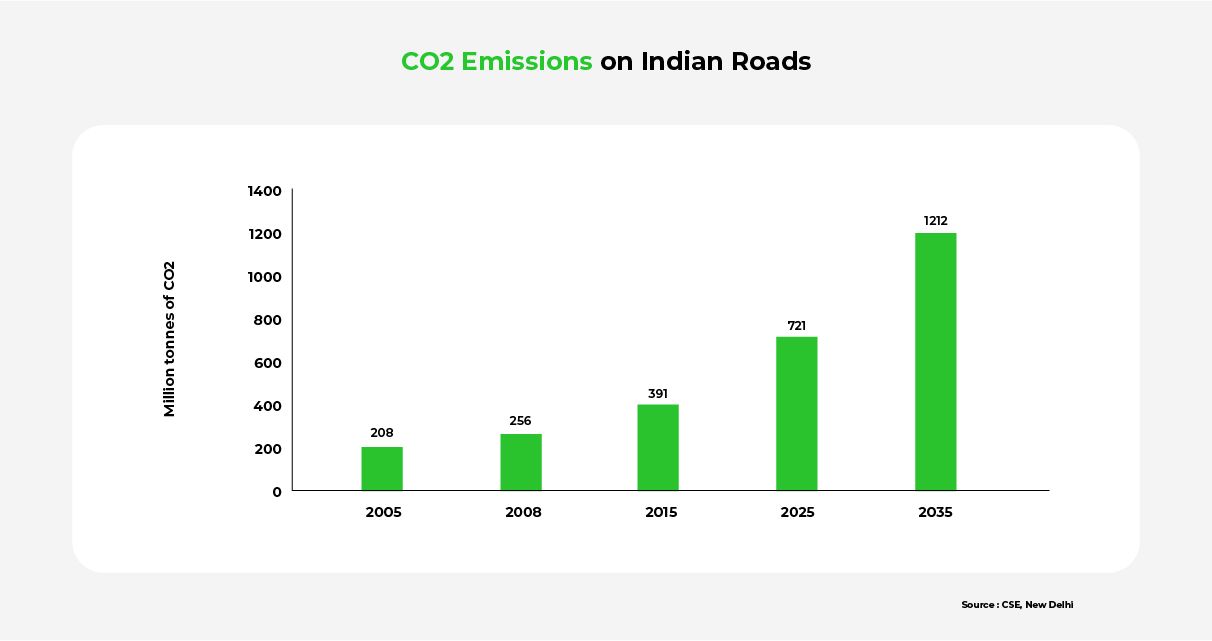
These challenges are a ticking bomb — as the graph above shows, vehicular emissions will increase dramatically in the coming decades. Recognizing the urgency, India’s government is actively pushing for increased adoption of EVs.
By reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, the positive environmental impact of EVs can help mitigate the negative impacts of the transportation sector on the environment.
How EV Adoption Can Benefit India’s Environment
EVs have great potential to address India’s pressing environmental challenges. By reducing harmful emissions, increasing the demand for renewable energy sources, and fostering sustainable production and disposal practices, EVs hold the key to revolutionizing India’s transportation sector.

Below, we analyze three positive environmental impacts of EVs.
1. Reducing Resource Depletion with EVs
EVs benefit the environment insofar as they require fewer natural resources to produce than traditional vehicles. EVs have simpler mechanics than petrol or diesel vehicles.
Furthermore, their batteries can be recycled, minimizing the need for new resources and reducing waste. By creating more demand for EVs, potential EV owners can reduce the environmental impact of extensive mining and nonrenewable resource depletion.
2. EVs as a Solution to Air Pollution
Unlike traditional vehicles, EVs do not produce tailpipe emissions, which are harmful air pollutants. By utilizing electricity stored in batteries to power their electric motors, EVs eliminate the need for combustion engines that rely on fossil fuels.
Furthermore, EVs employ regenerative braking, which sends energy generated by braking back to the car’s power system. ICEs, on the other hand, use disc brakes that emit even more pollution.
Knowing the environmental impact of EVs can help potential car buyers make informed decisions and promote EV adoption in their communities — leading to more benefits for the country.
3. EVs and Climate Change Mitigation
EVs can be charged using electricity generated from renewable sources like solar panels and wind turbines. Unlike traditional sources of electricity, renewable sources don’t emit greenhouse gasses that contribute to climate change.
EV owners, RWAs, and businesses can work together to establish renewable energy infrastructure to power EVs in their communities, further improving the environmental impact of EVs
India needs to develop and implement sustainable government policies that effectively incentivize all stakeholders to embrace EVs and push for a greener future for the country’s transportation.
By doing so, India can pave the way for a dynamic EV revolution that not only addresses environmental challenges but also unlocks countless economic and societal opportunities for generations to come.
Stakeholder Roles in Driving EV Adoption & Sustainability
Maximizing the environmental impact of EVs cannot happen without a collaborative effort involving policymakers, businesses, governments, and individuals. Each party plays a crucial role in creating a political and economic environment that supports the adoption of EVs.
Below we take a top-down look at four key players, and how they can work together to ensure India can reap a positive environmental impact from EVs.
1. Policymakers and Government Initiatives
Policymakers should create favorable policies and regulations that promote the installation of renewable energy sources for powering EVs. They can also provide incentives and support to accelerate the transition to clean energy. Doing so will help increase the positive environmental impact of EVs.
2. Businesses and Green Innovation
Businesses can work alongside governments to boost EV adoption. In particular, they can invest in research and development for renewable energy sources and materials. They can also sponsor events to raise awareness about the need for end-to-end green mobility options. They can also promote eco-friendly living by offering charging amenities at their premises to boost EV adoption.
3. Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs)
Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs), along with individuals, can take advantage of government subsidies to establish solar-powered charging infrastructure in their communities.
They can also contribute to the safe disposal of EV batteries by establishing collection hubs in their communities. One by one, RWAs can promote the environmental impact of EVs and boost EV adoption in their communities and across the country.
4. EV Owners and Consumers as Change Agents
Lastly, current and potential EV owners can make their voices heard. They can demand that EV makers use renewable materials, encourage their housing communities and offices to install solar panels for charging, and use their purchasing power to support EV manufacturers in driving the shift towards sustainable transportation.
Projected Environmental Benefits of EVs in India by 2030
Partnerships among the roles above complement India’s push for renewable energy. Specifically, India is currently the world’s largest producer of bioenergy. The country is also expected to become the third-largest producer of ethanol — an alternative clean energy source that can be used to power EVs — by 2026.
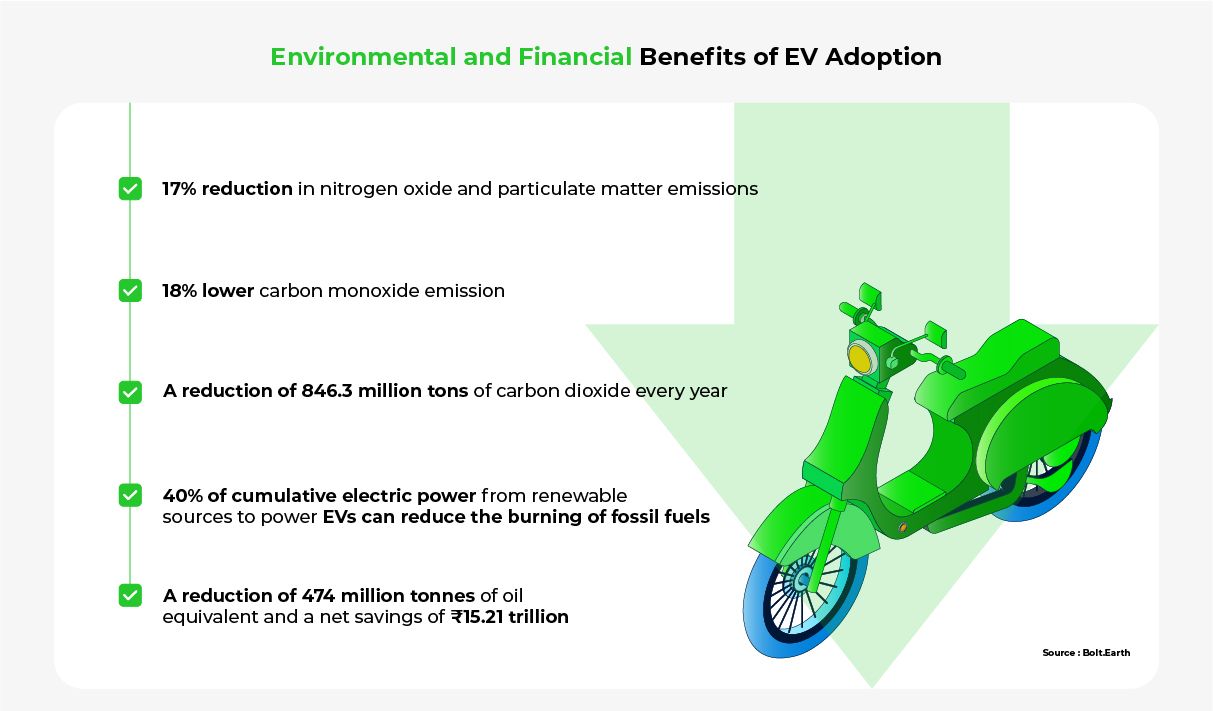
Due to these concerted efforts, the environmental impact of EVs by 2030 is looking bright:
- 17% reduction in nitrogen oxide and particulate matter emissions
- 18% lower carbon monoxide emission
- A reduction of 846.3 million tons of carbon dioxide every year
- 40% of cumulative electric power from renewable sources to power EVs can reduce the burning of fossil fuels
- A reduction of 474 million tonnes of oil equivalent and a net savings of ₹15.21 trillion
As India continues to transition to clean energy sources for EV charging, the environmental benefits will continue to grow. Widespread EV adoption, coupled with investment in charging infrastructure and renewable energy sources, can help India achieve its climate goals while promoting sustainable and responsible development.
Driving Towards a Sustainable Future with EVs
Currently, the transportation sector environment in India severely impacts the environment by contributing to resource depletion, air pollution, and climate change. India’s adoption of EVs holds immense potential to address these pressing environmental challenges and pave the way for a sustainable transportation future.
EVs require fewer natural resources for production and can be manufactured using renewable materials, minimizing resource depletion. Additionally, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing harmful air pollutants that can cause adverse health effects. EVs can also be charged using electricity generated from renewable sources, such as solar and wind power, thereby achieving a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and their impact on climate change.
To ensure a successful transition towards EVs, collaborative efforts are crucial. Policymakers can create favorable policies and regulations that promote renewable energy infrastructure and provide incentives for EV adoption. Similarly, businesses can invest in research and development for renewable energy sources, charging infrastructure, and eco-friendly EV manufacturing practices.
By embracing EVs and promoting a greener future for transportation, India can simultaneously address environmental challenges, unlock economic opportunities, and improve the well-being of current and future generations. Ultimately, a collective effort from all stakeholders can enable India to realize the positive environmental impact of EVs and achieve a sustainable and responsible path for development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the expected growth rate of EVs in India by 2030?
The expected growth rate of EVs in India by 2030 is around 49% per year. EV sales are predicted to reach 10 million per year by 2030. The Indian government is targeting 30% electrification of all vehicles by 2030.
How will the government’s policies influence the adoption of EVs in India?
Government policies, such as tax breaks, can incentivize car owners to switch to EVs. Subsidies and the single window system can encourage RWAs and small businesses to set up EV charging stations. Furthermore, business-friendly policies can boost domestic EV manufacturing and the generation of renewable energy.
What are the potential challenges in the widespread adoption of EVs in India?
Potential challenges in EV adoption include lack of charging infrastructure, high battery costs, limited driving range, and a lack of consumer awareness and education about EVs. The affordability of EVs also remains an additional concern for many consumers.
How will the shift towards EVs impact the automotive industry in India?
The growing demand for EVs will drive investments in research and development, battery manufacturing, EV software development, and charging infrastructure. Domestic manufacturing of EVs and components will also create new job opportunities and support the country’s economic growth. However, the shift towards EVs will also require significant investments in retooling manufacturing facilities and upskilling the workforce to adapt to the changing technology.


Mar 05, 2026 • EV Charging Infrastructure
The Hidden Cost of Poor Electrical Design in EV Charging Networks
Read More



