The Role of OEMs in Driving Platform Integration within OS
Raghav Bharadwaj
Chief Executive Officer
Published on:
02 Nov, 2023
Updated on:
06 Oct, 2025

In today’s dynamic auto industry, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are driving innovation and progress. Traditionally, they have designed, developed, and produced various components of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. As the world shifts towards software-defined vehicles, however, their role is evolving to include building and deploying elements within the automotive operating system (OS) for a seamless user experience.
Automotive OS forms the backbone of a car, managing and controlling functions including braking, infotainment, and safety. This means that OEMs must master increasingly complex car elements, such as sensors. Meanwhile, incompatibilities and poor harmonization among software car elements pose significant issues. If left unaddressed, these issues can hinder innovation and impede electric vehicle (EV) adoption, leading to environmental and economic setbacks.
Within that context, this article explores the following questions:
- How do OEMs contribute to designing, integrating, and ensuring compatibility among platform elements within automotive operating systems?
- What challenges are involved in integrating platform elements within an automotive OS, and how can OEMs overcome them?
- How can harmonization of platform elements within automotive OS transform the automotive industry by improving user experience, accelerating innovation, enhancing safety and security, and facilitating connected and autonomous vehicle technologies?
The Current Landscape of Automotive OS Platform Elements
The current landscape of automotive OS platforms is highly fragmented. Typically, OEMs manufacture some components, purchase some from partners, and build some through joint ventures. Once all the elements are ready, OEMs integrate them into a proprietary platform for a car.
Today’s leading players include Google’s Android Automotive and Apple’s CarPlay. As expected, Google’s platform integrates with Android phones while CarPlay integrates with iPhones. Meanwhile, Tesla’s proprietary operating system provides seamless connectivity for Tesla vehicles, and Blackberry’s QNX is steadily increasing its market share. Other prominent players include AGL, Baidu, BMW, Continental, COVESA, Ford, GM, Siemens, Benz, Toyota, Microsoft, and Volkswagen. The automotive OS market reached USD 5.7 billion in 2022, and is projected to increase to USD 19.5 bn in 2032 — an impressive annual growth rate of 13%!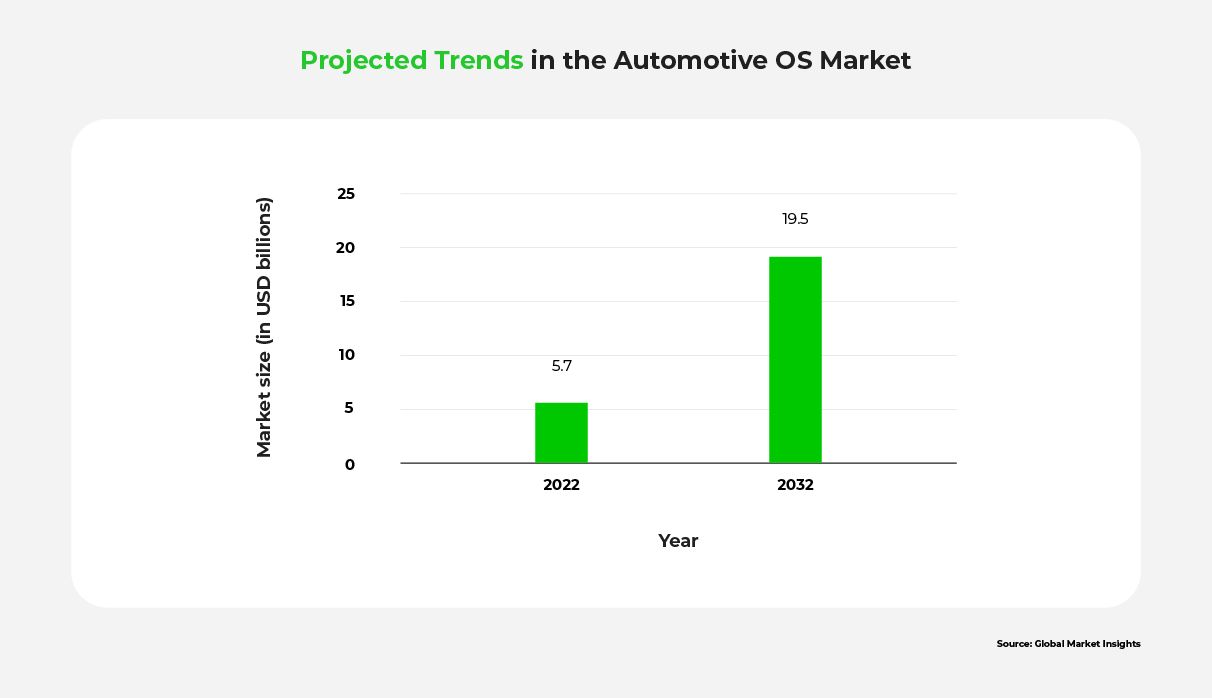
However, capitalizing on this high growth rate will not be easy for OEMs, given the rapid technological advancements, user demands, and lack of standard protocols across software platforms. In particular, the ever-growing number of software components and the need to communicate between in-car and cloud-based platforms further complicate software development. A promising solution to scale and overcome these impediments is to focus on harmonizing the different elements for cohesive functionality and greater synergy.
The Need to Harmonize Platform Elements
The existing fragmentation among automotive software platforms and standards poses a challenge for all EV stakeholders, particularly OEMs. Traditional gasoline-powered vehicles were primarily hardware-driven, but current and future vehicles are increasingly replacing hardware with software to control and manage various functions. As a result of this shift, OEMs have been investing more resources to adapt their applications and services to work on different OS platforms.
As vehicle models proliferate and software functions become more complex, however, these investments lose scalability. A better option is to prioritize integrating and harmonizing disparate software elements. By adopting such a strategy, OEMs can:
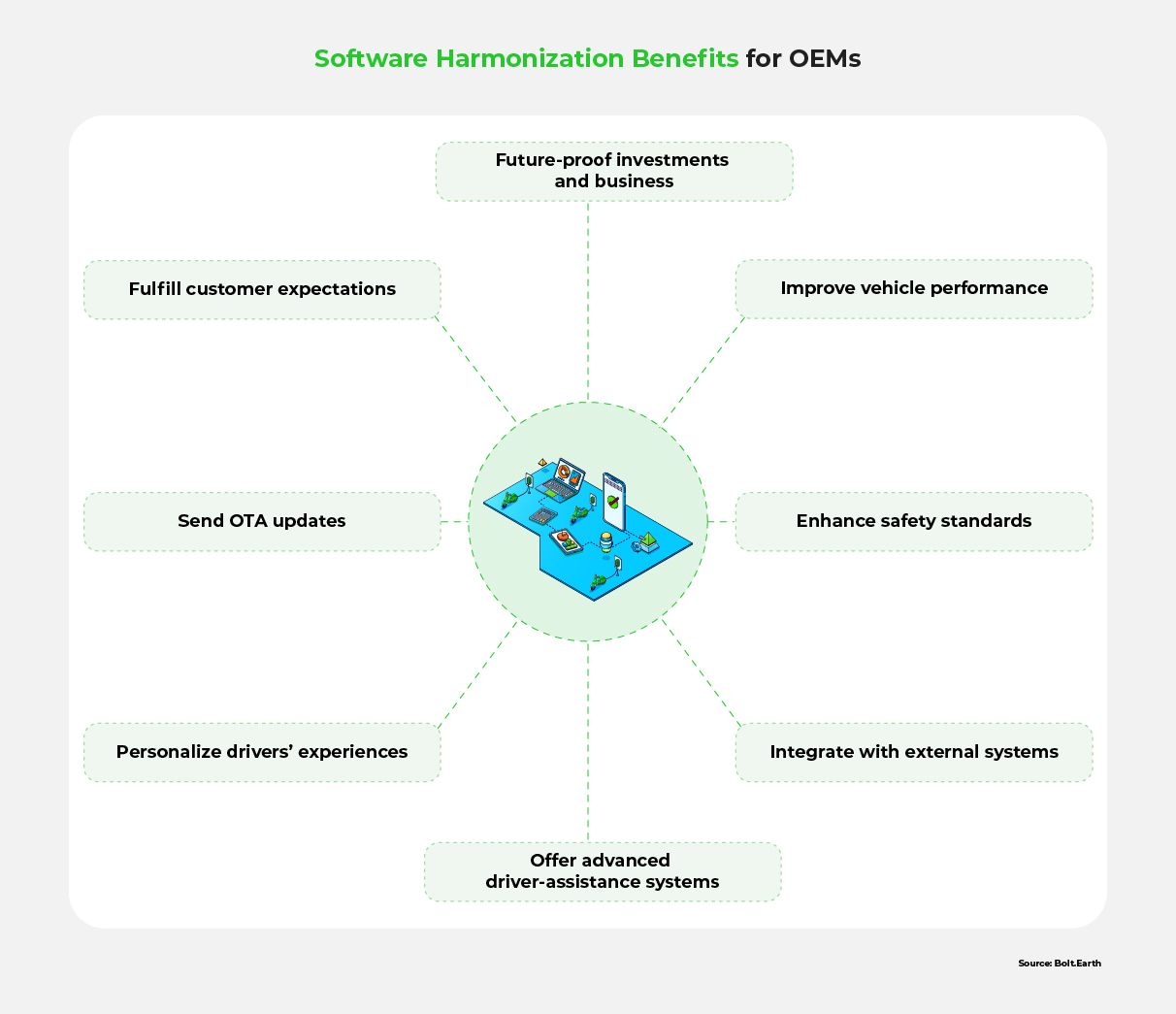
To realize these benefits, it is crucial for OEMs to adapt their strategies and priorities toward harmonization.
The Role of OEMs in Platform Elements
Given OEMs’ pivotal role in building software systems, they have the unique opportunity to turn the existing harmonization challenges into beneficial opportunities. Here are various elements that OEMs can enhance to propel growth in the automotive OS domain while focusing on scalability and security.
Designing and Integrating Platform Elements
Design is the first step in software development, and, by prioritizing harmonization, OEMs can ensure that they create designs based on hardware and software components that work cohesively. From infotainment systems and connectivity modules to sensors and control units, OEMs can design a system that enables smooth connectivity and integration.
Ensuring Compatibility and Interoperability
In the world of software-defined vehicles such as EVs, cars are seen as devices. Just as computers and smartphones need compatible apps, cars need systems that can communicate and collaborate. Standards like AUTOSAR attempt to ensure this interoperability, but each electronic control unit (ECU) is still built individually. OEMs must strive to use common protocols that ensure compatibility with other software apps and interoperability with diverse hardware components.
Collaborating with Software and Technology Partners
Collaboration with software and technology partners enables OEMs to leverage external expertise with minimal upfront research costs. With this approach, OEMs can enhance their software capabilities, accelerate innovation, and keep pace with rapidly evolving technologies. Sharing knowledge and experience among different stakeholders of software-defined vehicles can lead to creating a universally-compatible OS with cutting-edge features, robust security, and a superior user experience.
Conducting Testing and Validation
Rigorous testing and validation of platform elements within the automotive OS give OEMs the opportunity to verify functionality, performance, and safety standards, and to identify and address any potential issues or vulnerabilities before vehicles reach consumers. By adhering to stringent testing protocols, OEMs can ensure that the platform elements, which include electronic control units, sensors, IoT units, and mobile apps, meet the highest quality standards and deliver a reliable and secure user experience.
Providing Ongoing Support and Updates
Providing ongoing support and software updates, along with addressing customer feedback and preferences, are important processes which OEMs must plan in advance. In particular, cybersecurity best practices must be geared for EVSE devices, communications with EVs, and upstream devices like cloud, third-party apps, and software of grid operators. By continuously monitoring and addressing likely security threats, OEMs can release timely bug fixes, security patches, and feature enhancements to adapt to evolving user needs and ensure the long-term performance and functionality of the OS.
Collaborating with Industry Stakeholders
OEMs must work with industry stakeholders, including regulatory bodies and standards organizations, to shape industry standards, protocols, and guidelines for interoperability and compatibility among diverse vehicles and systems. These efforts can empower OEMs to drive the overall advancement of the automotive OS landscape and ensure a cohesive and standardized approach to platform integration.
Although many OEMs are working towards harmonization, many integration challenges stand in the way.
OEMs’ Platform Integration Challenges
All emerging technologies create complexities, and software-defined cars are no exception. Advances in automotive software are not only enhancing next-gen cars’ capabilities, but also creating numerous integration challenges for OEMs.
Diverse Hardware Configurations Across Vehicles
Each vehicle model and brand may have unique combinations of processors, memory capacities, connectivity modules, and sensor configurations. These variations among car models make it difficult for OEMs to design software that works seamlessly across diverse hardware configurations. More importantly, such incompatibilities can lead to safety and security issues. As a result, OEMs must continue to invest resources in developing software that can adapt to varying computing capabilities while efficiently utilizing available hardware resources.
Compatibility Issues with Third-Party Applications
Third-party applications, like navigation systems or infotainment platforms, are often developed by different software providers, each with their own interfaces, data formats, and compatibility requirements. To integrate them, OEMs must perform compatibility testing for smooth interactions between the OS and third-party software. Even with extensive testing, however, compatibility issues can still arise when OS updates or changes impact the functioning of third-party applications. A possible solution is for OEMs to collaborate closely with software partners to maintain compatibility and address any issues.
Compatibility Issues with Legacy Systems
OEMs face challenges when integrating new platform elements with legacy systems in older vehicles. Legacy systems may have different communication protocols, software architectures, and hardware limitations. Ensuring backward compatibility with legacy systems can be complex and may impose limitations on system updates and advancements. OEMs need to carefully balance the need for backward compatibility with the desire to introduce new features and technologies, as it may be necessary to maintain support for legacy systems while gradually phasing them out in favor of more advanced platform elements.
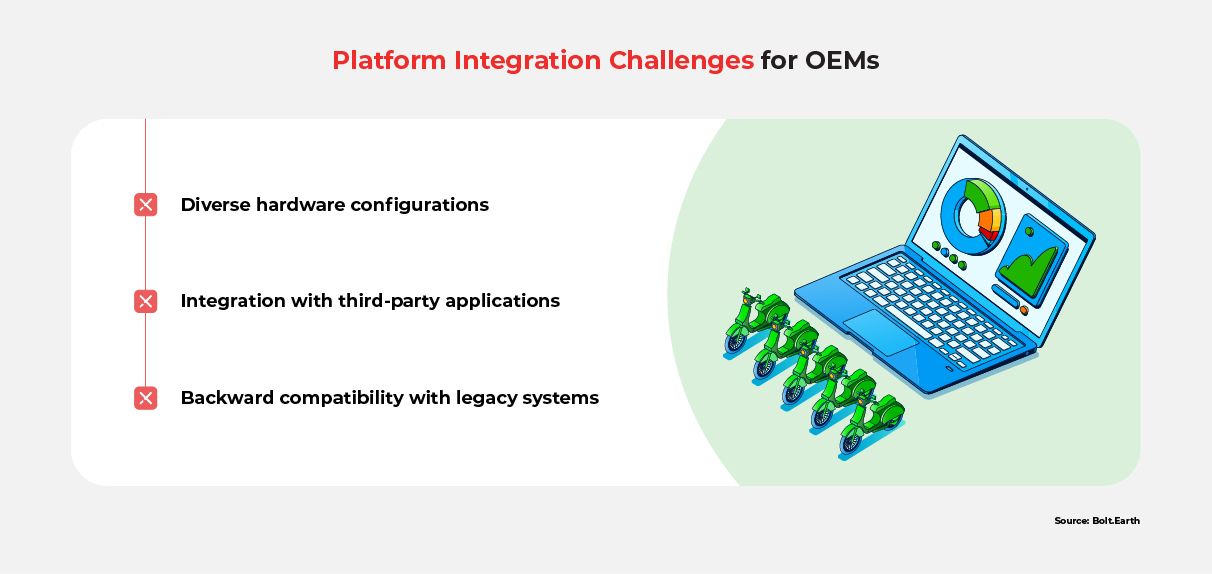
Addressing the above challenges is difficult, but not impossible. With the right strategy and concerted effort, OEMs can overcome them.
Overcoming OEMs’ Platform Integration Challenges
OEMs need innovative solutions and strategic approaches to overcome their platform integration challenges. Some key strategies that OEMs can use are:
Over-The-Air (OTA) Software Updates
Through over-the-air (OTA) updates, OEMs can remotely deliver new software features, security enhancements, and bug fixes to vehicles. This contributes to user convenience by minimizing the need for in-person servicing. Additionally, OTA updates offer cost savings for OEMs by reducing recall expenses and enabling swift deployment of critical updates. They can also resolve compatibility issues with third-party applications and legacy systems. However, OEMs must implement robust security measures and rigorous testing and validation processes to ensure the reliability and stability of OTA updates before deployment.
Collaboration and Standardization Efforts
Collaborative efforts among OEMs, software companies, and technology providers are critical for establishing common standards and specifications for platform integration. These industry stakeholders can come together to define common interfaces, protocols, and data formats that promote interoperability and compatibility across different vehicles and systems. Industry alliances or organizations such as the COVESA (formerly GENIVI) Alliance or the Automotive Grade Linux (AGL) project, which focus on ensuring harmonization within automotive OS, are working on such standards. Additionally, collaborations and partnerships foster knowledge sharing, promote best practices, and enable the development of robust and harmonized solutions for automotive OS.
Modular and Scalable Platforms
Building a modular architecture makes it easy for OEMs to integrate new platform elements without disrupting the entire system. They can add or replace components with minimal impact on the overall system, ensuring flexibility and scalability. Application programming interfaces (APIs) are vital in enabling seamless integration of third-party applications and services. Well-documented and standardized APIs facilitate interoperability among different software components, enabling easy integration and enhancing the overall user experience. These modular designs also promote scalability, so existing hardware can adapt to evolving software configurations, processing capabilities, and future technological advancements.
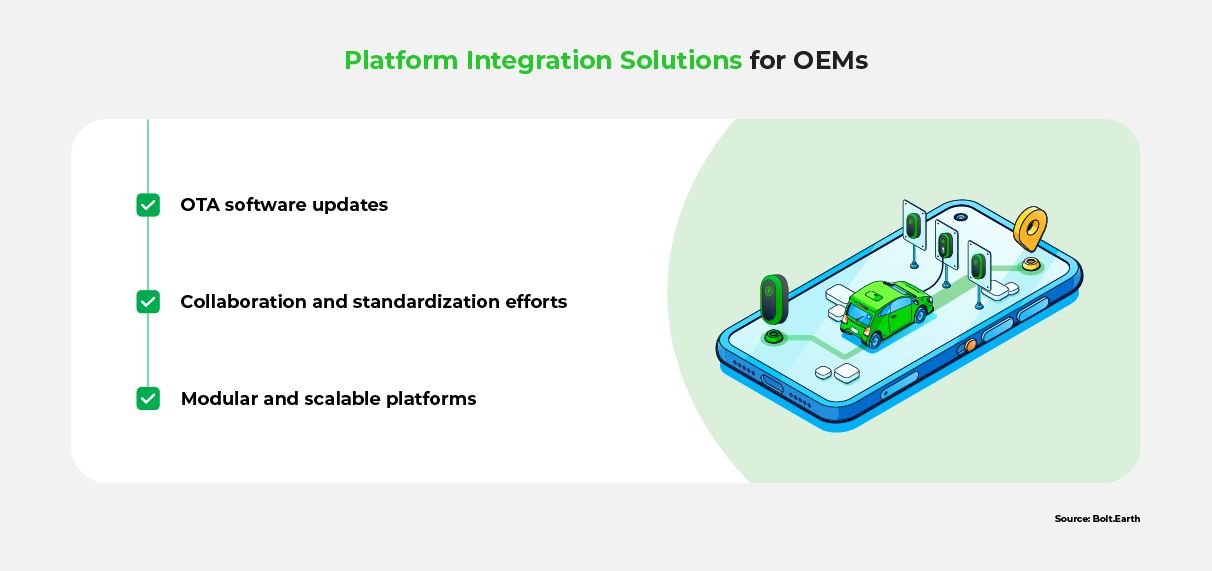
The above solutions can significantly assist OEMs, and the larger auto industry, in leveraging the benefits of software development and technological advancements.
The Impact of Harmonized Platform Elements Within Automotive OS
By driving the harmonization of platform elements, OEMs can shape the future of the entire auto industry as a whole. For example, their efforts can promote:
Faster Development and Deployment of New Features
Platform harmonization permits OEMs to streamline the development and deployment of new software features and updates. A harmonized platform provides a standardized framework for software development, thereby reducing the complexity and time required to develop new features across different vehicle models and brands. This enables OEMs to accelerate innovation, improve their time-to-market, and more efficiently deliver advanced features and functionalities to customers.
Enhanced Safety and Security
Harmonized platform elements lead to improved safety and security of vehicle systems and data. Standardized security protocols and robust software architectures enable OEMs to establish a strong foundation for cybersecurity. Additionally, harmonized platforms enable faster deployment of security patches and updates that can enhance the overall security posture of vehicles. Through such efforts, OEMs can build trust with customers and prioritize their well-being.
Facilitation of Connected and Autonomous Vehicle Technologies
In a harmonized platform, sensors, connectivity modules, and control units work together to provide a superior user experience. Furthermore, such harmonization enables the automotive OS to efficiently process, analyze, and share data for real-time traffic updates and predictive maintenance. These features enhance the usability of vehicles and can lead to their wider adoption.
All of the above benefits create a unified ecosystem that empowers society to enjoy the positive environmental and economic effects of software-defined vehicles.
Fostering a Unified Approach Towards EV Software
The harmonization of platform elements holds the potential to create an automotive landscape that improves users’ driving experience by providing them with cutting-edge technology. Moreover, harmonized platform elements enhance vehicle systems’ and data’s safety and security. Though many challenges exist in harmonizing diverse car elements, OEMs can overcome them with the right strategy and active collaboration with other stakeholders to implement standardized security protocols and robust software architectures.
Additionally, with seamless communication and interoperability among different vehicle systems and external networks, OEMs can unleash the full potential of these technologies. This can enable the creation of advanced features, improve efficiency, and foster a more interconnected and intelligent automotive software ecosystem, as well as economically benefiting OEMs by bolstering car sales and providing a competitive advantage. As the industry evolves, OEMs will remain at the forefront, strengthening a unified approach toward EV software to realize a connected, autonomous, and electrified future.
For more information about harmonization, please see the FAQ and Resources below!
FAQ
How do OEMs ensure compatibility and interoperability among different platform elements?
OEMs can implement standardized protocols to ensure compatibility and interoperability. They can also work with other players to establish guidelines and specifications for enabling seamless communication and integration between various components and systems.
How does harmonization enhance the user experience in vehicles?
Harmonization of car elements leads to consistent and intuitive user interfaces, standardized features, and interoperability with third-party applications and services. Overall, it promotes a unified and cohesive experience, enabling users to easily navigate and utilize various functions and technologies within the vehicle.
How do OEMs collaborate to achieve platform integration?
OEMs can collaborate with software companies, technology providers, and industry organizations to establish common standards and specifications for platform integration. This collaboration involves knowledge sharing, joint research and development, and participation in industry alliances or organizations dedicated to promoting harmonization within the automotive industry.
How do OTA updates contribute to seamless software integration?
OTA updates enable the remote delivery of software updates to vehicles, eliminating the need for physical changes to hardware components. Besides adding to user convenience, OTA updates also make it easy to access the latest features and build a secure system.
What security measures are in place to protect against vulnerabilities in platform integration?
Security measures including encryption secure data transmission while authentication mechanisms like multifactor authentication ensure authorized access to data and systems. Additionally, code signing to verify software integrity, intrusion detection systems to identify potential threats, and continuous monitoring for timely identification and response to security incidents can protect cars from cyberattacks.
How does platform harmonization advance connected and autonomous vehicle technologies?
Platform harmonization enables seamless communication and interoperability among different vehicle systems and external networks. Harmonized platforms allow vehicles to exchange data with infrastructure, other vehicles, and cloud-based services. Such an approach can ease the development and deployment of advanced features.
Resources
McKinsey: The Case for an End-to-End Automotive-Software Platform
Discover how software can transform the automotive industry.
EE Times: Perspectives on Automotive Operating Systems
Gain a detailed understanding of automotive operating systems.
Automotive World: How can OEMs Accelerate the Software-Defined Mobility Revolution?
Learn about OEMs’ impact on SDV adoption.
European Commission: Technical Harmonization
Find out about Europe’s technical harmonization guidelines, which provide a model for other countries.
Center for Automotive Research: Global Harmonization of Connected Vehicle Communication Standards
Explore the latest efforts to harmonize vehicle elements.


Feb 27, 2026 • EV Technology and Trends
Renewable Energy and EV Charging in India: Technical Integration [+ Challenges]
Read More


