What is Smart Parking? The Rise of EV Charging & IoT in Real Estate
Raghav Bharadwaj
Chief Executive Officer
Published on:
23 Sep, 2025
Updated on:
28 Jan, 2026

India’s cities are facing a parking crunch. Smart parking has emerged as a tech-driven solution to this urban dilemma, leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and connectivity to make parking spaces more efficient. At the same time, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming real estate, from residential complexes to commercial buildings, by increasing demand for charging infrastructure.
This blog dives into the facts, data, and trends shaping the future of parking and mobility. Specifically, it answers three key questions:
- What exactly is smart parking, and why is it essential in modern cities?
- How is EV charging transforming parking in real estate projects?
- What role does IoT play in enabling smarter, data-driven real estate and urban planning in India?
What Exactly Is Smart Parking, and Why Is It Essential in Modern Cities?
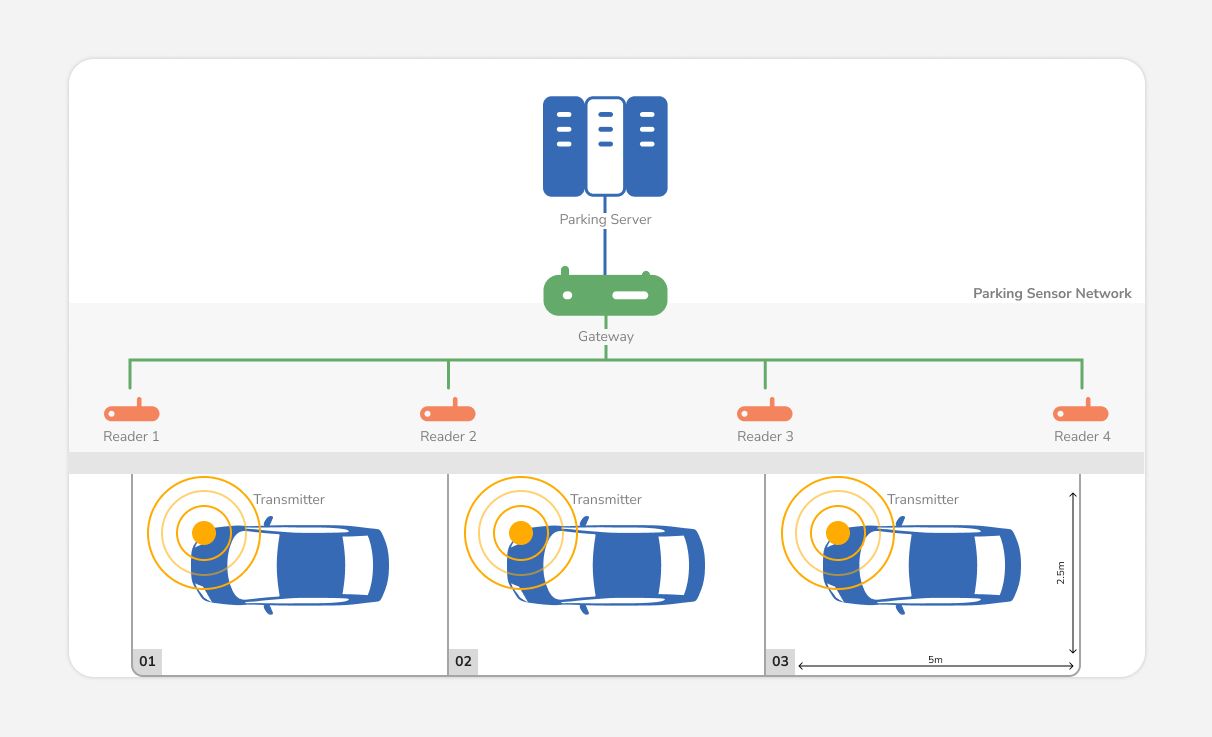
Smart parking refers to parking systems that use sensors, cameras, and connectivity (IoT) to monitor parking space occupancy in real time and guide drivers to available spots. Drivers can check a mobile app or street display to see which spots are free or even get turn-by-turn directions to the open space in complex garages. This real-time occupancy data reduces the search time for users and reduces frustration.
Key technologies enabling smart parking include:
- IoT Sensors and Cameras: Ultrasonic or magnetic sensors and AI-enabled cameras detect occupancy and transmit data wirelessly.
- Cloud Platforms: The sensor data is transmitted to cloud-based parking management platforms. This allows aggregating data across a city or building and applying analytics, which is increasingly relevant for EV charging for buildings and smart infrastructure.
- User Applications and Digital Signage: Mobile apps and digital signage help drivers locate and reserve spots. For example, a mobile app can display available parking in a given area and allow reservations. In some Indian cities like Davanagere, a municipal app lets motorists reserve parking spots in advance and get real-time availability updates, which has helped streamline traffic and improve access to smart EV charging stations.
- Automated Payments: Contactless payment systems, often integrated with FASTag (the RFID toll payment sticker) to enable drive-in/drive-out payments without manual tolling. This reduces queues at exits and eliminates cash leakage. It also enables dynamic pricing models (varying rates by demand or duration) to encourage turnover and optimize charging solutions for businesses.
- Analytics and Management Software: IoT-based parking solutions generate a wealth of data, including peak usage times and average park durations. City authorities or private operators can use this data to optimize parking policies, adjust pricing, and plan future capacity. Over time, such data-driven management leads to better land use.
In essence, smart parking brings the power of IoT and data to an age-old urban problem. It reduces search time and enhances user experience while improving operational efficiency. It’s a win-win: drivers save time and fuel, and owners maximize utilization. This has tangible environmental benefits too; shorter parking searches mean fewer cars idling and circling, which in turn cuts fuel consumption and tailpipe emissions.
Notably, smart parking often overlaps with smart building and smart city initiatives. For instance, India’s Smart Cities Mission has funded projects for sensor-based smart parking in multiple cities, integrating them with central command centers to better manage traffic flows and support EV charging for buildings.
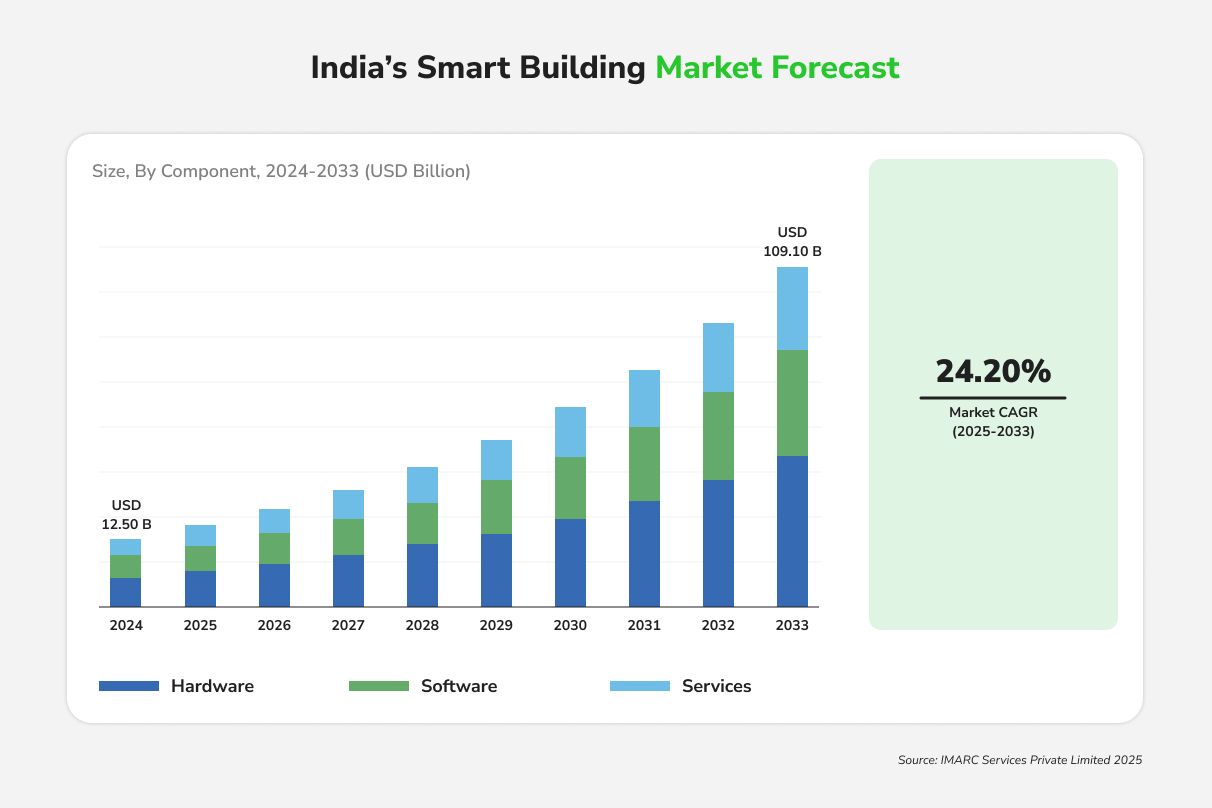
The broader smart building market in India, including parking, was about USD 12.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 109 billion by 2033.
Why Smart Parking Matters in Urban India
Urbanization and vehicle growth have led to severe parking shortages and traffic congestion. India alone has over 300 million vehicles on the road, and as cities grow vertically, traditional parking methods are becoming obsolete. Studies show that up to 30% of city traffic is caused by drivers searching for parking. This not only wastes time and fuel but also contributes significantly to pollution and economic loss. In fact, urban India loses an estimated ₹1.5 lakh crore (₹150 trillion) annually to traffic congestion, with parking-related issues accounting for nearly a third.
Smart parking can reduce the time spent searching for parking by up to 50% and triple garage capacity through automation. Globally, the smart parking market is projected to grow from USD 5.7 billion in 2024 to USD 14.1 billion by 2033 (about 10.5% CAGR).
Automating parking operations (through sensors, cameras, and digital payments) cuts labor costs and boosts revenue per space by optimizing utilization. Real-time data from IoT sensors provides accurate availability info, minimizing idle empty spots and helping operators adjust pricing based on demand, a model increasingly adopted in EV charging solutions for businesses. In short, smart parking promises more parking capacity with fewer resources and less chaos.
How EV Charging Is Transforming Parking In Real Estate Projects?
The explosion of electric vehicles globally is another major factor driving the evolution of parking infrastructure. Electric cars need charging points – and unlike a gas station that you visit only occasionally, EV owners often charge where they park (at home, work, or shopping centers). This convergence of parking and charging has huge implications for real estate developers and city planners.
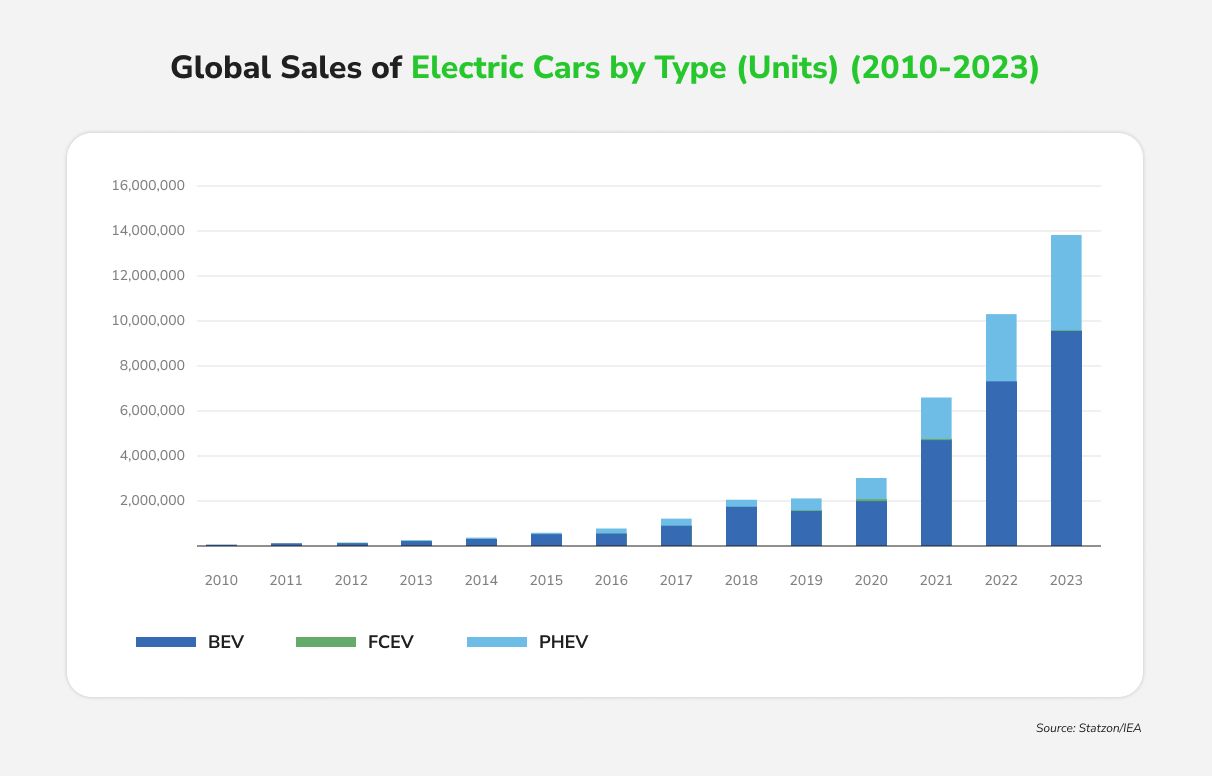
The convergence of parking and charging is reshaping real estate. Unlike gas stations, EV owners typically charge where they park (at home, work, or shopping centers). This shift demands that parking infrastructure evolve into charging infrastructure, making it a central concern for developers and city planners focused on planning EV charging for real estate.
In 2023, global EV sales neared 14 million, a 35% jump from 2022, bringing the global fleet to 40 million vehicles. India saw 80,000 electric cars sold in 2023, a 70% year-on-year increase. While EV penetration is still modest, the government’s 2030 targets are ambitious: 30% of private cars, 70% of commercial vehicles, 40% of buses, and 80% of two- and three-wheelers. If realized, that’s 80 million EVs on Indian roads—each needing a place to park and charge.
Such growth will require an extensive EV charging network, and much of that charging infrastructure will be in parking areas. Globally, the number of public EV chargers is projected to grow fourfold from approx. 4 million in 2023 to over 15 million by 2030. A joint report by FICCI and McKinsey estimates that ₹16,000 crore (approx. $2 billion) in investments will be needed by 2030 to meet the country’s EV charging demand. These chargers are being installed in a variety of real estate contexts, from highway rest stops and shopping mall parking lots to office campuses and apartment basements.
For real estate developers, providing EV-friendly parking is quickly shifting from a niche amenity to a mainstream requirement. Recognizing this, the Indian government and regulators have issued new guidelines:
- The Model Building Bye-Laws 2016 (adopted by states like Karnataka and Maharashtra) requires 20% of parking capacity in new buildings to support EV charging. Housing societies must allow residents to install private chargers as per the Ministry of Power guidelines, it is considered a “legal right” of the consumer now. This policy push is accelerating the retrofitting of existing parking spaces with chargers, from multi-level apartments to office complexes.
- Many municipal authorities are updating parking policies to include EV charging. For example, Delhi’s draft parking rules provide discounted fees for EVs in public parking lots, and cities like Bengaluru and Mumbai are exploring “EV-only” parking zones in crowded areas to encourage cleaner vehicles (as part of pollution control strategies).
The integration of EV charging with smart parking systems is a natural next step. Since smart parking apps already manage parking spot availability, adding the status of charging stations to these platforms makes life easier for EV owners. We are seeing features like real-time EV charging slot booking through parking apps, so drivers can reserve a space that has a charger ahead of time. Additionally, advanced parking management systems now incorporate dynamic pricing for EV charging, for instance, higher rates during peak hours or incentives for vacating a charging spot once the car is topped up. This prevents charger hogging and optimizes the usage of each unit.
Another interesting trend is the move towards sustainable parking infrastructure for EVs. Some parking lots are installing solar-powered EV charging stations (solar canopies over parking stalls with integrated chargers), reducing the draw on the grid and aligning with green building goals. This is particularly relevant in sunny parts of India; a few metro cities have piloted solar parking lots that generate renewable energy for on-site charging.
What Role Does IoT Play in Enabling Smarter, Data-Driven Real Estate and Urban Planning in India?
From the perspective of real estate owners and urban planners, the confluence of IoT and EVs in parking brings several tangible benefits:
- Enhanced User Experience and Convenience: Imagine entering a mall parking garage and your smartphone (or car’s navigation) immediately directs you to an open spot equipped with an EV charger. No circling ramps, no anxiety about whether you’ll find a plug. This level of convenience, enabled by IoT sensors and connectivity, greatly improves the visitor experience. It also builds customer loyalty; frustration-free parking can be a selling point for a shopping center or office building. Moreover, features like contactless payments and app-based reservations mean drivers can seamlessly park and pay without fumbling for cash or tokens.
- Higher Property Value and Revenue Streams: Incorporating smart parking and EV charging can make a property more attractive. A commercial building with an IoT-driven parking system can advertise higher efficiency and guaranteed spots for tenants. On the revenue side, property managers can earn income from EV charging fees and better utilize every parking stall via dynamic pricing. A smart parking system can increase overall parking revenue by adjusting rates based on demand and preventing misuse or fraud. Essentially, technology turns parking from a cost center into a smarter profit center.
- Reduced Congestion and Emissions in and around the Property: Studies in Indian cities have shown that deploying sensor-based smart parking (along with intelligent traffic management) can significantly cut down on vehicles prowling the streets for parking, thus easing bottlenecks. A well-known fact is that IoT-guided parking systems can reduce city driving emissions by minimizing the search time and idle running of engines. This contributes to cleaner air and aligns with climate action goals. In a concrete example, a smart parking pilot in Chandigarh (as part of the Smart City initiative) covering dozens of zones is expected to reduce average parking search time by 30-40%, translating to smoother traffic flow and lower fuel waste.
- Better Security and Compliance: IoT in parking can bolster security through surveillance and access control. License plate recognition cameras can automatically log entries/exits and flag unauthorized vehicles. Sensors can detect if someone is parking in an EV-designated spot without an EV and alert authorities or apply fines. These measures protect resident parking in mixed-use developments and ensure that the infrastructure (like EV chargers) is used fairly. Additionally, having digital records of parking usage helps enforce time limits and prevents issues like parking ticket fraud or revenue leakage, which were common in fully manual systems. As EV charging for buildings becomes standard, these compliance tools will be essential to ensure fair access and proper usage.
- Data-Driven Urban Planning: Over the long term, the data collected by smart parking systems is incredibly valuable for city planners and developers. Patterns of parking occupancy by time of day, by location, and even by vehicle type can inform how future garages are designed. Planners can identify underutilized lots that could be repurposed or pinpoint areas where demand far outstrips supply to justify building new multi-level parking. This data can feed into broader models of transportation and land use, helping answer questions like whether adding a metro station or bus route near a busy parking area reduces car usage. In essence, smart parking turns the parking lot into a source of insights for smarter urban development.
India’s Trajectory vs. Global Trends
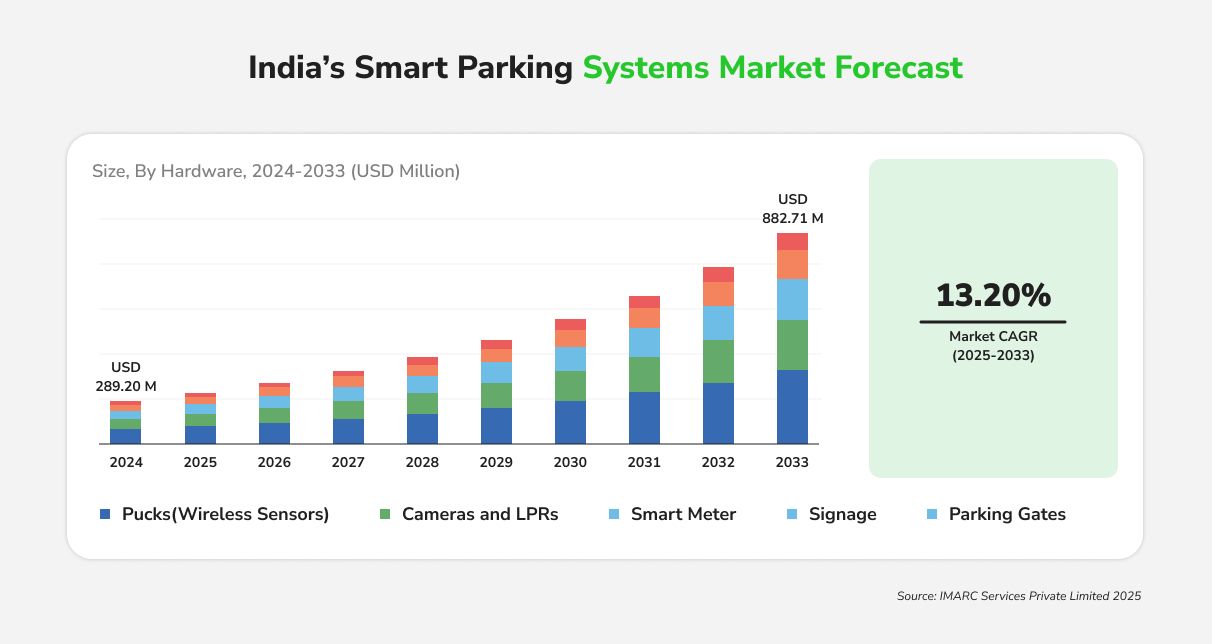
India’s smart parking market was valued at USD 289 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 883 million by 2033. Government initiatives like the Smart Cities Mission have catalyzed adoption with cities like Puri (Odisha) and Davanagere (Karnataka) deploying advanced systems featuring IoT sensors, license plate recognition, and FASTag integration.
India particularly stands out for the emphasis on two-wheelers and three-wheelers in the EV revolution. Unlike Western countries, a huge share of India’s urban commuters use scooters, bikes, and auto-rickshaws. Consequently, “smart parking” in India must cater to these vehicles as well, providing secure, organized parking and charging for electric two-wheelers. Cities are exploring dedicated two-wheeler smart parking zones with e-charging stations (for e-bikes) and anti-theft IoT locks. This broadens the definition of smart parking beyond just car garages.
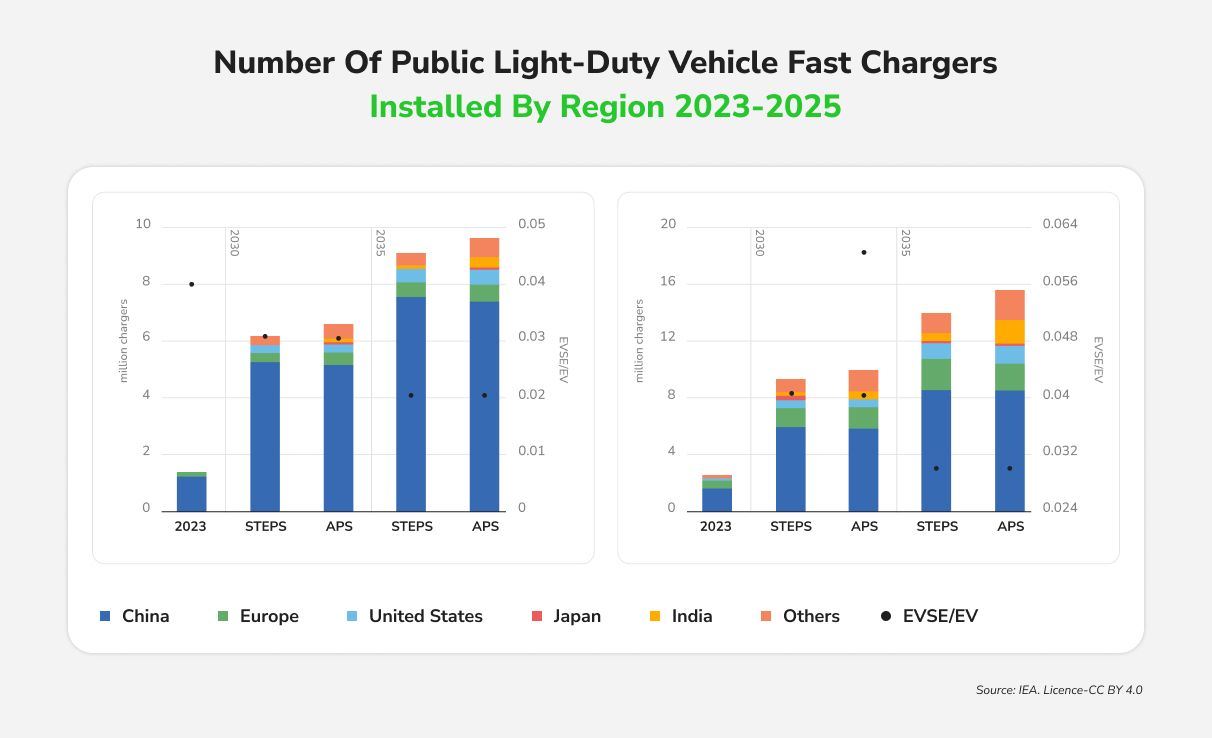
Globally, countries are innovating with app-based parking payments and dynamic pricing to discourage long stays in prime spots. For example, San Francisco’s early smart parking project (SFpark) used demand-based pricing and sensors to reduce parking search time and was cited as a model for congestion reduction. China leads in public EV charging, while Europe and the US are exploring “mobility hubs” that integrate parking, charging, and shared transport.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the intersection of smart parking, EV charging, and real estate will only grow tighter. By 2030, India’s cities could be vastly different in terms of mobility. If EV adoption reaches the intended targets, tens of millions of EVs will need convenient charging.
Most charging (up to 80%) is expected to happen at home or work, which means buildings must become the new fuel stations. We can expect every new apartment complex, office tower, and mall in India to incorporate networked EV chargers in their parking layout. In fact, only about 55% of Indian car owners today have access to home charging, so expanding to workplace and public charging is crucial. Real estate developers who provide abundant charging infrastructure stand to attract this growing EV owner demographic.
On the technology front, IoT and AI will make parking even smarter. We might see AI-driven predictive parking, where algorithms predict parking availability at your destination by learning from historical data and current traffic and proactively reserve a spot for you. Some global cities are already testing systems that guide drivers not just to a parking lot but to a specific floor and slot based on the size of their vehicle, all optimized in real time. Autonomous vehicles could further disrupt parking; if self-driving cars become common in later decades, they might drop passengers off and then park themselves in ultra-dense robotic parking facilities. While that scenario is still on the horizon, it underscores the need to design parking infrastructure that’s adaptable.
From a sustainability perspective, integrating renewable energy and energy management into parking will gain traction. Parking garages with solar rooftops, battery storage, and smart charging management can help balance the grid load of EVs. During the daytime, solar panels could directly power EVs in the lot; at night, the charging systems might communicate with the grid to draw power during off-peak hours. The IoT connectivity in these systems will be essential to manage such complexity, ensuring that as vehicles, buildings, and the grid all talk to each other, the outcome is optimal for everyone.
In conclusion, smart parking represents a confluence of multiple innovation streams, urban digitalization (IoT, data analytics), the clean mobility transition (EVs), and next-gen real estate development.
India, with its massive urban challenges and tech-savvy population, is fertile ground for these solutions. We are already seeing the early benefits: reduced congestion, better user experience, and new business models around parking. As the data and case studies build up, stakeholders from government bodies to private developers are gaining confidence in scaling up smart parking projects.
The rise of EVs makes the case even stronger. A parking spot is no longer just a patch of concrete; it is a potential energy node where vehicles plug in and cities manage electricity demand. This will require continued collaboration between automakers, utilities, urban planners, and tech providers. The road ahead might be long, but one thing is clear: the future of parking in India and across the world is smart, connected, and electric. Embracing smart parking and IoT in real estate today is a step toward cities that are both more livable and more sustainable tomorrow.



Mar 05, 2026 • EV Charging Infrastructure
The Hidden Cost of Poor Electrical Design in EV Charging Networks
Read More


