How Are EVs Shaping India's Urban Future?
Raghav Bharadwaj
Chief Executive Officer
Published on:
21 Aug, 2023
Updated on:
09 Mar, 2026

Smart cities represent the new frontier of urban sustainability. Equipped with cutting-edge technology, they are shaping the future of communities globally. A key feature of these modern urban landscapes is the integration of electric vehicles (EVs), contributing to more efficient and eco-friendly transportation systems.
India, with the launch of its ambitious Smart Cities Mission (SCM) in June 2015, is marching forward in this global trend. Its vision includes a significant focus on adopting EVs as a critical aspect of its urban sustainability plan.
In this article, we’ll discuss how electric vehicles and smart cities can work together to create a more sustainable future for India. We’ll explore how EVs can help to reduce pollution and improve air quality, and how smart cities can make it easier for people to use EVs.
More specifically, this article answers these three questions:
- How can the integration of EVs help smart cities promote sustainable and efficient transportation?
- What are the challenges when integrating EVs into smart cities, and what solutions can overcome them?
- Why consider the potential future impact of integrating EVs to create smarter cities?
The Current State of Smart City Development in India
The concept of a smart city involves adopting data-driven technologies. These cities are designed to enhance energy efficiency, reduce environmental footprints, and elevate living standards.
The infographic below showcases the smart solutions that can be integrated within smart cities. This clarifies why smart cities are a noteworthy, desirable development for the urban population.
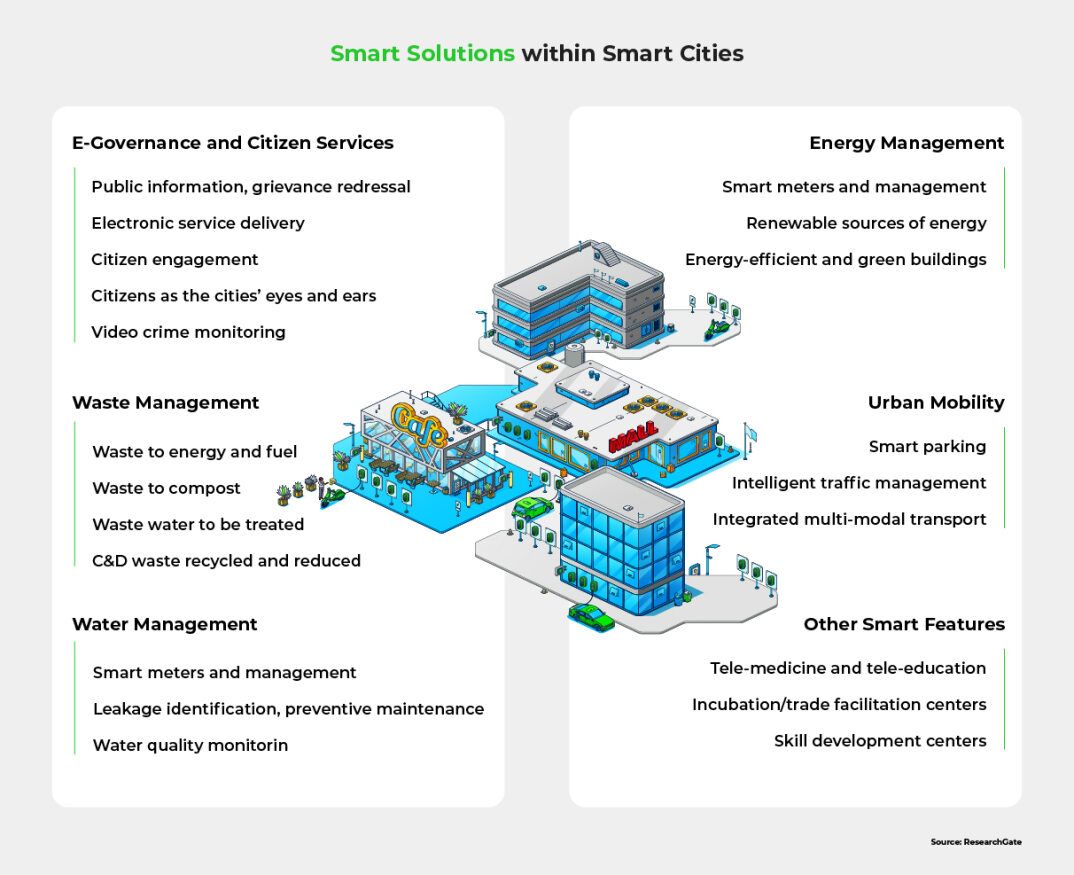
Smart City Development in India
As a result of rapid urbanization rates, a smart city initiative in India is pivotal to improving urban living. In 2015, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the Smart Cities Mission. It aims to transform 100 cities into urban ecosystems with robust infrastructure, a sustainable environment, and innovative solutions that reflect the citizens’ aspirations.
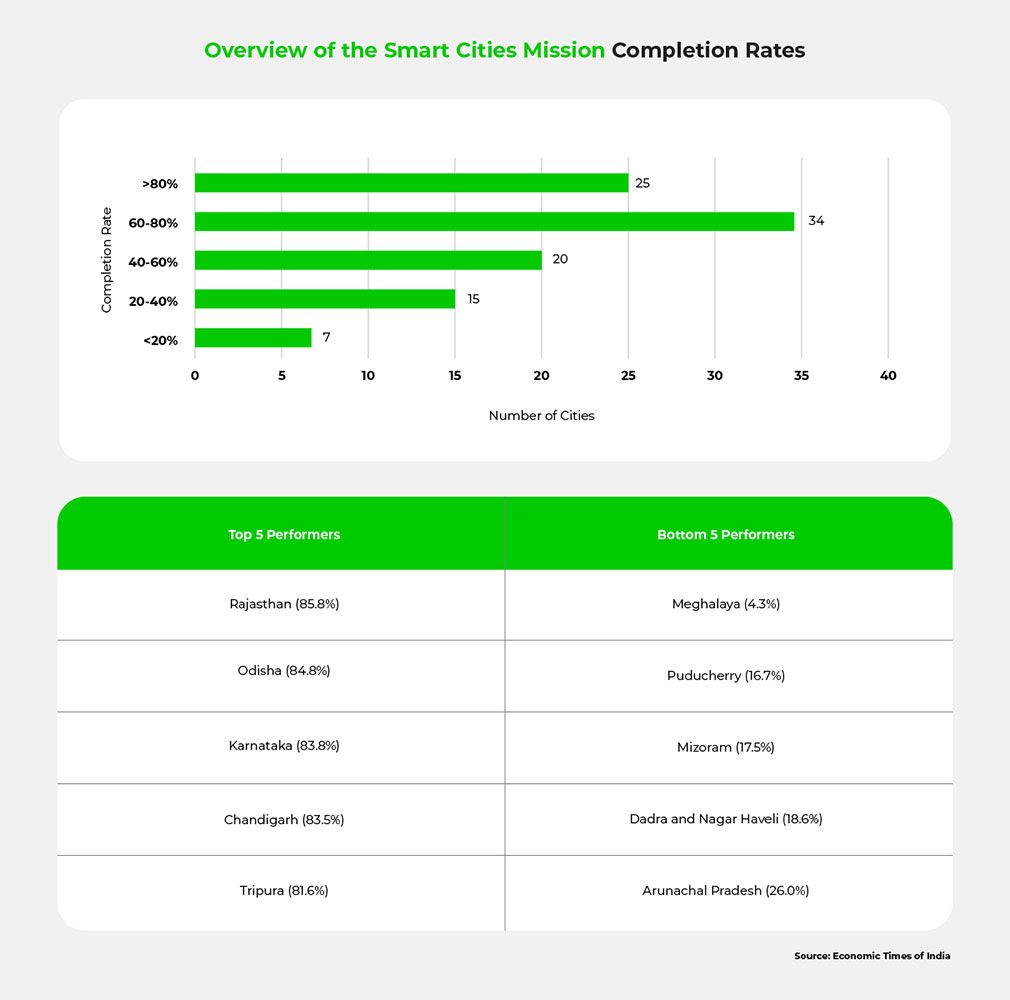
COVID-19 slowed progress, but momentum has returned. As of mid-2025, 72% of smart city projects are completed nationwide, with big cities averaging 80% and smaller cities around 66% completion, respectively.
Smart cities are designed to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental footprint. and enrich living standards through data-driven technologies.
Why EVs Are Critical for Smart Cities
India’s rapidly growing megacities, such as Mumbai, Delhi, and Kolkata, face the complex challenge of balancing quality of life with environmental sustainability.
One critical aspect of this urban overhaul is the integration of EVs. By shifting towards electric vehicles, India stands to significantly reduce its reliance on fossil fuels, cut greenhouse gas emissions, and lessen the impacts of climate change.
This approach provides a blend of economic, social, and environmental benefits. As a result, the integration of electric vehicles into smart cities will be a key strategy for India’s urban future.
In the following sections, we delve into the general impact of EVs on building smart cities. We focus on three key areas that make integrating EVs into smart cities more desirable for India.
1. Economic Impact
Smart cities can have a significant impact on a country’s economy. More specifically, smart cities can help boost the economy in the following areas.
Job Creation and Skill Development
Building a smart city necessitates a skilled workforce. Key factors for attracting private investment and boosting employment include a business-friendly environment, an innovation-driven climate, and a strong network of educational and vocational institutions.
Within the EV industry, the importance of technology is paramount. EV manufacturing, R&D, and charging infrastructure create new employment opportunities.

Fleet and Logistics Transformation
EVs play a pivotal role in the adoption of smart city concepts, transforming transportation to be more sustainable. Electric buses and e-rickshaws lower costs and emissions. This can help improve transportation services in smart cities.
Furthermore, EVs support the logistics industry by reducing carbon footprint and enhancing last-mile deliveries.
Boost to Clean Energy
Smart charging integrates EVs into the renewable energy ecosystem. This can pave the way for efficient and sustainable energy management.
Combined with other smart initiatives like smart grids and smart energy management, smart cities can help boost or speed up the adoption of clean energy. This will help countries contribute to a greener energy industry.
2. Social Impact
Beyond providing a significant economic boost, smart cities also have a direct positive impact on citizens’ lives.
Improved Air Quality
Integrating EVs into smart cities helps curb greenhouse gas emissions and fosters a low-carbon energy future. The resulting improved air quality can alleviate respiratory diseases.
For example, a recent study found that transitioning Delhi’s existing bus fleet to all-electric buses could reduce the total pollutant emissions by 74%, helping reduce the number of premature deaths caused by air pollutants. 17% of annual deaths in India are due to air pollution.
Enhanced Mobility and Accessibility
The integration of EVs with smart traffic sensors enables real-time vehicle tracking. This can reduce congestion and accidents, facilitating smoother drives. Insights from this data can improve transportation planning.
Furthermore, smart cities enhance safety through camera surveillance and traffic signal sensors. At the same time, they optimize parking services for improved accessibility and mobility within the city.
Inclusive and Equitable Development
EVs foster clean transportation, reducing emissions and improving air quality, which benefits all citizens, particularly those with lower incomes. Smart city infrastructure, such as advanced charging systems and intelligent traffic management, enhances accessibility and inclusivity.
The growth of the EV industry generates jobs, supports economic growth, and prioritizes equity, inclusivity, and sustainability. This promotes a more equitable and inclusive future.
3. Environmental Impact
Most notably, EVs and Smart Cities can have a great impact on the environment, which is a benefit for the world, not just the smart city residents.
Conservation of Natural Resources
Smart city technology enables optimal resource allocation. Smart charging infrastructure, intelligent traffic management, and smart energy management systems are woven into the smart urban landscape.
This helps achieve better resource conservation, which promotes more environmental sustainability. It also helps ensure equitable distribution of resources.
Mitigation of Climate Change
As urbanization progresses, smart city technology aids in monitoring urban heat islands (UHIs) caused by heat-absorbing surfaces. This data-driven approach empowers cities to address UHIs effectively and tackle climate change.
In conjunction with EVs, smart cities support sustainable transportation, curbing greenhouse gas emissions and slowing the effects of climate change.
Reaching these benefits, however, is not an easy feat.
Challenges in EV Integration for Smart Cities
Integrating EVs into smart cities is gaining importance due to the increasing attraction towards alternative urban mobility paradigms. However, the road to revolutionized urbanization is riddled with obstacles.
Below, we dissect three of these obstacles and their implications on the future of EVs and smart cities.
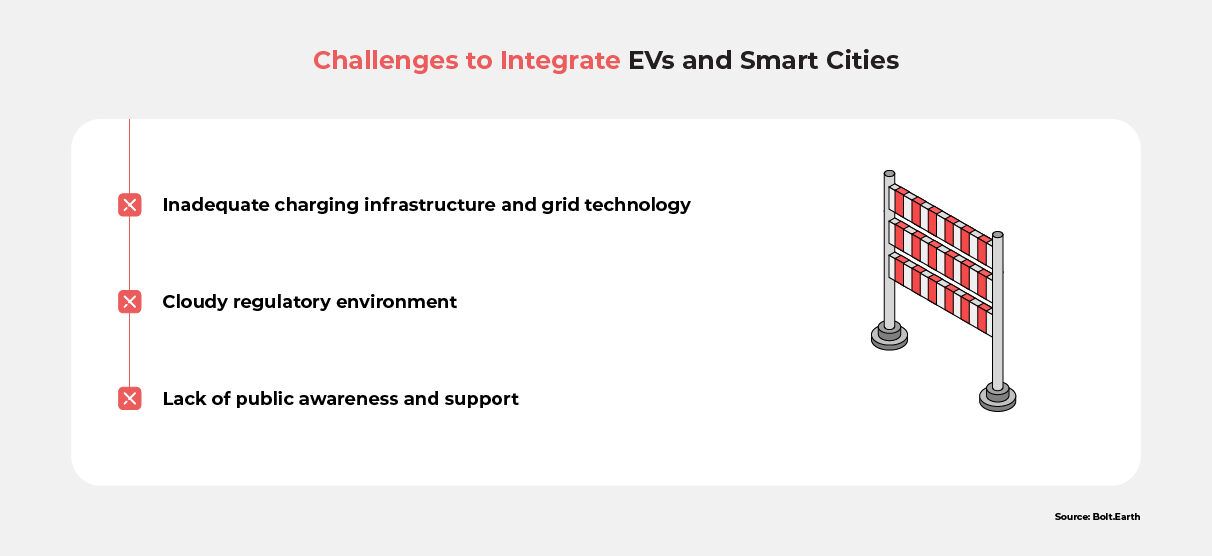
1. EV Charging Infrastructure Challenges
Charging infrastructure availability and maturity are essential aspects of driving EV adoption in any country. This also applies to the integration of EVs and smart cities.
Availability of Charging Infrastructure
In previous articles, we discussed India’s insufficient amount of public infrastructure in terms of high EV sales. As EV penetration increases in urban areas, uncoordinated charging may cause power outages.
In reality, an immature EV charging network also poses challenges. Existing charging facilities often offer limited services, lacking availability status and reservation options. EV users must search for available charging ports, leading to exhausting experiences and concerns in urban areas.
Grid Capacity and Stability
With EVs constituting a small fraction of the massive 362 million vehicle population, the current power grid adequately handles charging demand. However, a projected EV surge by 2030 could strain the grid, risking power outages and highlighting challenges posed by uneven electricity access and supply fluctuations.
This also applies to the emergence of more smart cities, which could possibly strain the grid even more with the integration of other advanced technologies.
Technology and Innovation
Technological knowledge and access to technology are crucial for smart city development. Scholars highlight the potential of technologies like IoT, Big Data, and AI for urban infrastructure, which includes EV charging infrastructure in Smart Cities.
However, a robust infrastructure of systems, devices, and communication networks is necessary to effectively capture, process, and disseminate data across different sources and support the integration of physical infrastructure.
The challenge lies in the advanced technologies required to realize Smart Cities, as well as addressing potential social impacts such as privacy concerns.
2. Policy Challenges
EV adoption is quasi-impossible without the backing of specific government policies. In a cloudy regulatory environment, the integration of EVs and smart cities will be more challenging.
Regulatory Instability and Inconsistency
To achieve the smart city vision, political stability, clear vision, and long-term planning are crucial. Transparent governance and citizen empowerment are also essential.
However, legal complexities, policy inconsistencies, and misalignment between central and state governments can hinder large-scale infrastructure development. This can further slow down the integration of EVs and Smart Cities.
Short of Municipal Government Capacity
Smart city applications have focused on surveillance and security, often managed privately. This is because Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) mostly rely on private funding. This is in line with the SCM’s prioritization of private partnerships, which aims to overcome municipal capacity limitations.
However, long-term smart city development requires building governance capacity and technological competence within municipal authorities to effectively manage projects. In the absence of municipal governments, integrating EVs and smart cities cannot be conducted smoothly.
Coordination between Central and State Governments
Among the governance barriers in smart city development are the absence of effective planning, communication, and leadership. Uncoordinated implementation and isolated efforts pose the risk of resource scarcity and project delays.
Complex organizational structures and political issues also contribute to a lack of internal coordination and cooperation within city agencies, hindering progress and collaboration. Without a unified approach and vision, the integration of EVs and Smart Cities will prove to be more challenging.
3. Public Acceptance Challenges
Because EVs and smart cities are projects for the people, they cannot succeed without the people’s support. Even if all else falls into place, integrating EVs into smart cities will not happen if the public remains opposed to these initiatives.
Below are some reasons why the public might have a negative perception of EVs and smart cities.
Consumer Behavior and Perception
The lack of transparency in policy-making processes undermines citizens’ trust in the government, impeding their willingness to support and engage with smart initiatives aimed at transforming cities for the better. In a word, citizens don’t feel they have any ownership in smart cities.
Lack of Awareness and Education
In terms of barriers, citizens are not aware of what is happening nor of the importance of their participation; consequently, the lack of citizens’ participation is a barrier to sustainable smart city development.
Solutions for Integrating EVs in Smart Cities
The Indian government’s initiatives and strategic partnerships have significantly boosted EV adoption and infrastructure development. However, the way ahead remains long. Furthering this progress calls for a multifaceted approach addressing infrastructure, policy, and public acceptance.
In the following sections, we will delve into three solutions for these areas, aiming to enhance the successful integration of EVs into India’s smart cities.
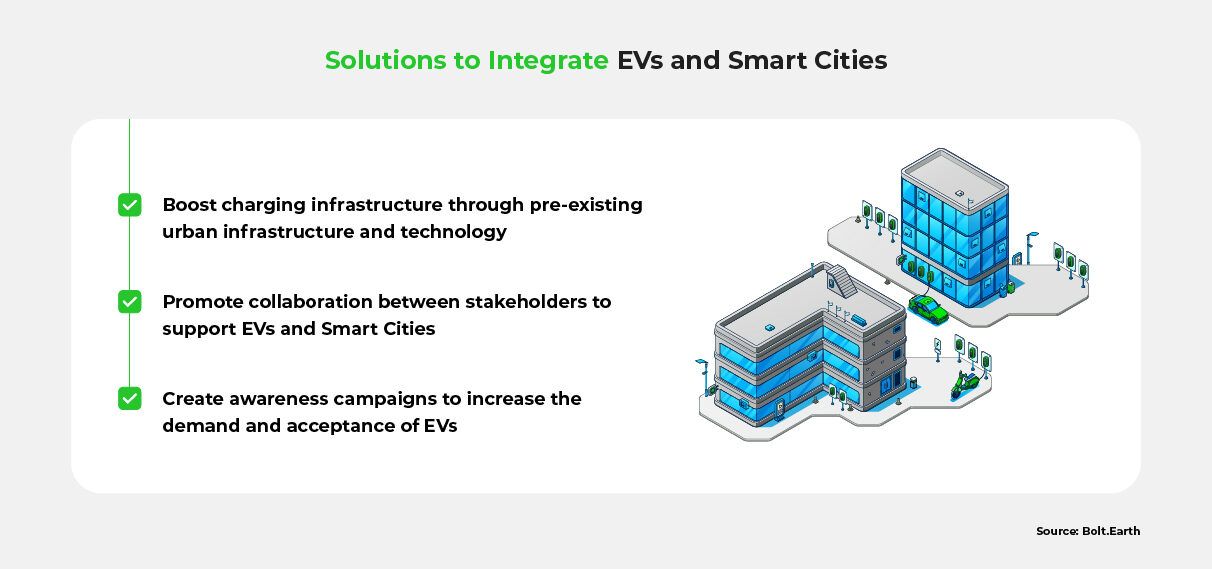
1. Integrate the EV Ecosystem into Smart City Technology
EV and smart city initiatives are mutually beneficial, supporting the development of both ecosystems. Below we look at some examples that can help India improve this symbiotic relationship, to further expand the reach of its charging infrastructure.
Adopt Smart Charging Stations with IoT
IoT plays a pivotal role in smart city technologies, including EV charging. It enables continuous monitoring, data reporting, and notifications for EV drivers, Charge Point Operators (CPOs), and network operators.
IoT also enables secure user authentication, including billing and transactions. Users can easily find and reserve available charging stations, receive real-time charging updates, and benefit from smart charging options based on energy rates.
IoT platforms can ensure efficient control and management of existing infrastructure. This can make the limited charging points available for more users. This will also enable the creation of a more connected charging network, with both private and public charging points and stations.
Leverage EVs to Promote Smart Energy Management in the Cities
Rapid urban growth drives high energy demand, surpassing local resources. The solution is a decentralized smart energy chain powered by renewables, ensuring sustainability and resilience through intelligent digital technologies.
Copenhagen’s EnergyLab Nordhavn project is a prime example. It shows how smart energy solutions, battery integration, EVs, and intelligent heating solutions can help enhance grid flexibility. Following this revolutionary city’s footsteps can help countries worldwide achieve carbon neutrality with the integration of EVs and smart cities.
Leverage Smart City Technologies for Enhanced Efficiency
EV charging infrastructure can utilize existing smart city infrastructure. Cities can repurpose parking spaces, fuel stations, and smart buildings as charging hubs. Bidirectional chargers can also enable efficient power management, facilitating power transfer between the grid and vehicles.
EVs are transforming parking lots into smarter spaces by integrating charging infrastructure, allowing real-time charging insights delivered to an app. Automated parking is also available, allowing owners to schedule a pickup from their phones.
For example, in Los Angeles, the innovative, cost-effective curbside Streetlight EV Charging Stations utilize existing infrastructure to meet the Mayor’s mandate for increasing EV adoption by adding 100,000 electric vehicles in the city by 2025. Similar hardware and software innovations can help integrate EVs into smart cities more seamlessly.
2. Support the Implementation of EV and Smart City Technology with Government Efforts
Clarifying the regulatory environment for smart city implementations requires coordination at different levels. This will help boost the stability in policies, as well as improve different authorities’ abilities to support Smart City projects.
The following best practices can help promote collaboration between institutions and governments:
- Collaborate with stakeholders: Foster coordination among governments, private entities, and the public to overcome administrative silos and promote accountability through e-governance services.
- Create Smart City plans for EV integration: Define the city’s vision and prioritize transportation improvement, aligning EV integration with Smart City goals.
- Develop strong partnerships: Collaborate with renowned organizations in technology, urban development, and policy to leverage expertise and ensure successful implementation.
- Seek additional funding through PPP: Mitigate risks and attract financing using tools like tax incentives, concession agreements, and Public-Private Partnerships. For example, the Anqing project in China partners with Qingdao TGOOD Electric to provide charging infrastructure using a viability gap funding model.
- Pilot test integration initiatives: Evaluate effectiveness and measure benefits before full-scale implementation.
- Assess, improve, and repeat: Continuously evaluate the rollout, gather feedback, and address inefficiencies for ongoing improvement and scalability.
3. Public Acceptance Solutions
As the end users of EVs and smart cities, the public needs to have more awareness to support integration initiatives. To gain citizens’ trust and support, some strategies should be adopted.
Create Consumer Education and Awareness Campaigns
To enhance customer awareness of EVs and smart cities, countries should create dedicated campaigns for educational purposes. These efforts educate on EV benefits, cost savings, environmental impact, and policies, promoting the shift towards sustainable mobility and smart urban environments.
Ampere Vehicles, for example, has been spearheading this movement. In 2021, the company announced a dedicated education campaign called “Ampowering Change”. This campaign aimed at boosting the demand for EVs in India by showcasing their benefits.
Then, in 2023, the company also created an anthem featuring Indian rappers to get more people to appreciate the electric revolution. With these initiatives, more people will be aware of the benefits of EVs, making them more likely to support the transition to EVs and Smart Cities.
The Path to Sustainable and Efficient Transportation in Smart Cities
In transitioning to sustainable urban development, EVs emerge as integral constituents. They bring about multifaceted benefits, socially, economically, and environmentally. Integration of EVs into smart city technologies, intelligent use of IoT for efficient charging, and creative reuse of existing urban infrastructure serve as promising solutions. Governmental efforts are pivotal; encouraging collaboration, fostering partnerships, securing funding, and promoting public awareness are all critical to this integration’s success.
Moreover, the public’s role is crucial; gaining acceptance and support ensures these initiatives’ sustainability. To make this sustainable, efficient, and inclusive urban environment a reality, we need concerted efforts from policymakers, industry leaders, and citizens. This joint effort will pave the way for the smooth integration of EVs into our smart cities, steering India towards a sustainable urban mobility future.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of integrating EVs within smart city technology?
Integrating EVs and smart city tech in India has multifaceted benefits: reduced emissions, improved air quality, and enhanced mobility. This can also lead to job creation and economic growth. These integrations also contribute to sustainable transportation, reduce fossil fuel reliance, and help achieve India’s environmental and economic goals.
How is the Indian government supporting the development of EVs and smart cities?
India’s government supports EVs and smart city development through various initiatives like the FAME II scheme and Production Linked Incentives for manufacturers. These efforts are designed to enhance charging infrastructure, subsidize EV adoption, attract private investment, and foster an environment conducive to sustainable urban development.
What infrastructure is needed for EVs and smart cities to be successful?
To successfully implement EVs and smart cities, we need charging stations, advanced energy management systems, and IoT-enabled smart grids. Other necessities include intelligent traffic systems, robust IT networks, data-sharing platforms, and communication systems.


Mar 05, 2026 • EV Charging Infrastructure
The Hidden Cost of Poor Electrical Design in EV Charging Networks
Read More


