Innovative Financing Models for India's EV Charging Infrastructure
Raghav Bharadwaj
Chief Executive Officer
Published on:
07 Jul, 2023
Updated on:
06 Oct, 2025

As India aims to accelerate its transition to electric mobility, the development of a robust and extensive EV charging ecosystem becomes paramount. However, by 2030, the nine largest cities are projected to need 46,397 public charging stations — highlighting the increasing demand for charging infrastructure.
The success of India’s shift to sustainable transportation relies heavily on the country’s ability to establish accessible and affordable EV charging infrastructure. Innovative EV infrastructure financing models can play a vital role in facilitating the affordability, scalability, and private sector involvement required to develop a comprehensive nationwide charging network.
In this article, we delve deeper into the following questions:
- What are the current financing challenges for EV infrastructure in India, and why is it important to address them?
- How can innovative EV infrastructure financing models boost EV adoption in India?
- Why are these innovative financing approaches likely to be effective for India, and what is their potential impact?
Current State of India’s EV Charging Infrastructure
In 2012, the Indian government launched the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020 (NEMMP-2020) with the goal of achieving an annual sales figure of 6-7 million EVs in the country by the end of the decade.
To support this mission, the Department of Heavy Industry (DHI) developed the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme. The graph below highlights the potential outcomes of these initiatives.
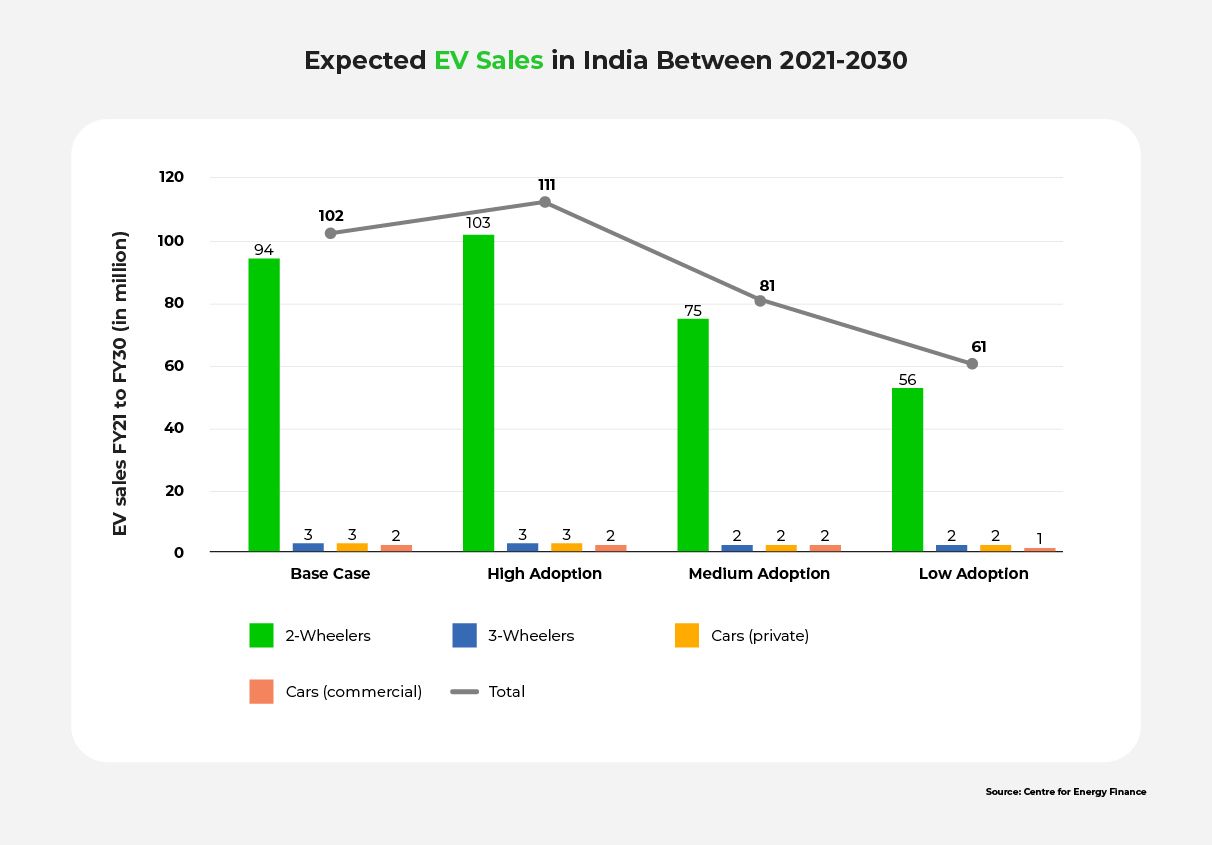
During Phase-I of FAME, the Ministry of Heavy Industries authorized approximately 520 EV charging stations at the cost of around Rs. 43 crore. Similarly, other incentives and subsidies were offered to foster the growth of the EV ecosystem.
In Phase II of the FAME India Scheme, a budget allocation of Rs. 1,000 crore was designated for a five-year period ending in 2024, dedicated to the establishment of charging infrastructure.
Moreover, the Ministry of Heavy Industries has also issued Rs 800 crore to the public sector oil marketing companies, tasking them with the installation of 22,000 EV charging stations across the country by 2024.
Currently, 6,586 public charging stations in India cater to over 2 million EVs. FAME-II plans to establish 2,877 charging stations across 68 cities and 1,576 charging stations along nine expressways and 16 highways. Among the states, Delhi has the highest number, with 1,845 available. However, there’s still considerable ground to cover before the policy target is achieved.
As challenges and areas for improvement are identified, comprehensive financial models can bridge the gap between availability and the projected requirements while ensuring affordability, adaptability, and speedy deployment of charging infrastructure.
Examining India’s Goals
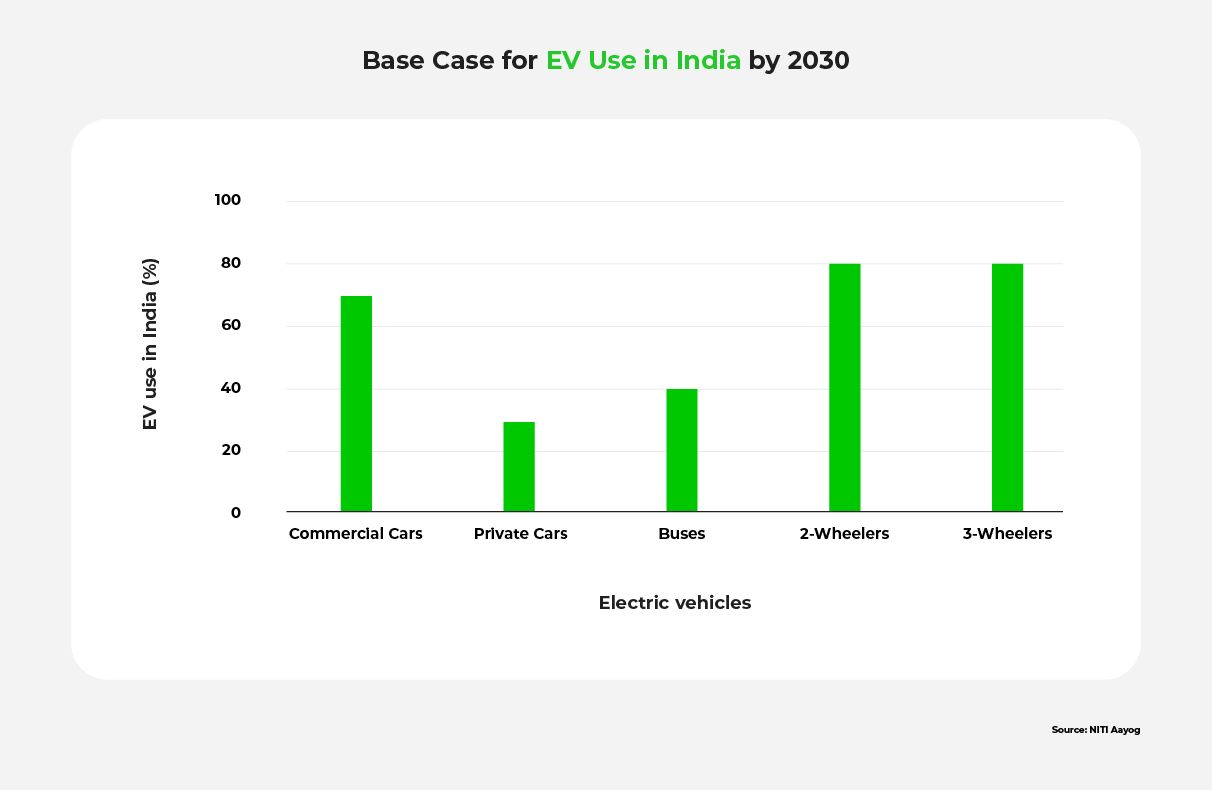
India is targeting 30% EV penetration by 2030, which will rely on a robust network of charging stations to soothe EV users’ range anxiety. Financing plays a key role in facilitating convenient and affordable access to public EV charging facilities.

According to the Centre for Energy Finance, India requires a network of 29,38,000 public chargers to meet its 2030 EV vision, with low capacity chargers contributing for 71% of the network. This projection is based on multiple factors, including projected GDP growth, the automobile industry’s contribution to GDP, and the penetration of EVs. This vision for 2030 outlined by NITI Aayog, a government-linked think tank, serves as the base case scenario.
Challenges of Infrastructure Funding
Adequate charging infrastructure is pivotal in driving the transition towards EVs. It provides the necessary convenience for potential buyers and EV users. However, establishing a network of charging stations requires substantial upfront investment, including the cost of land and equipment. Funding EV charging infrastructure in India poses a significant obstacle to the widespread adoption of electric EVs in the country.
To encourage private companies to invest in EV structure development, a stable and predictable regulatory environment is crucial. With a clear forecast of EV charging demands and revenues, private companies can confidently commit their resources to these projects. Current uncertainty over EV charging demand and revenues, however, leaves companies hesitant to invest in charging infrastructure ventures.
Below we examine three challenges in financing India’s EV infrastructure:
1. Bridging the Funding Gap
Investors are finding it increasingly difficult to estimate EV project costs and revenue. India’s Centre for Energy Finance estimates a requirement of Rs 20,600 crore (USD 2.9 billion) worth of funding for India to meet its public charging needs. Another study predicts investments upwards of Rs 1 lakh crore by 2032, to cater to the growing demand for EVs, which is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 39%. Additionally, long payback periods, high upfront costs, and uncertain return on investment further complicate the development of viable business models, deterring potential investment.
2. Governmental Challenges
The Indian government faces budgetary constraints and competing priorities as it allocates funds across various sectors, including healthcare, education, and infrastructure development. These limitations restrict the available funding for developing charging infrastructure.
3. Challenges for the Private Sector
High capital costs associated with setting up EV infrastructure pose a significant challenge for private sector investment decisions, especially when uncertain returns on investment and evolving business models for charging stations further complicate investment decisions. Financial incentives such as grants, subsidies, or low-interest loans can help alleviate the burden of high capital costs for private companies and encourage private sector investment.
To overcome these challenges, innovative public-private partnership models and collaborative arrangements can make a significant difference. These models, like revenue-sharing agreements or performance-based incentives, can help align the interests of public and private entities.
Financing Models to Promote EV Infrastructure Funding
Innovative approaches to EV infrastructure financing in India have the potential to attract private sector investment, bridge the funding gap, and support widespread EV adoption.
These approaches offer promising opportunities to secure necessary capital, ensuring the development of a comprehensive EV ecosystem that meets the growing demand.
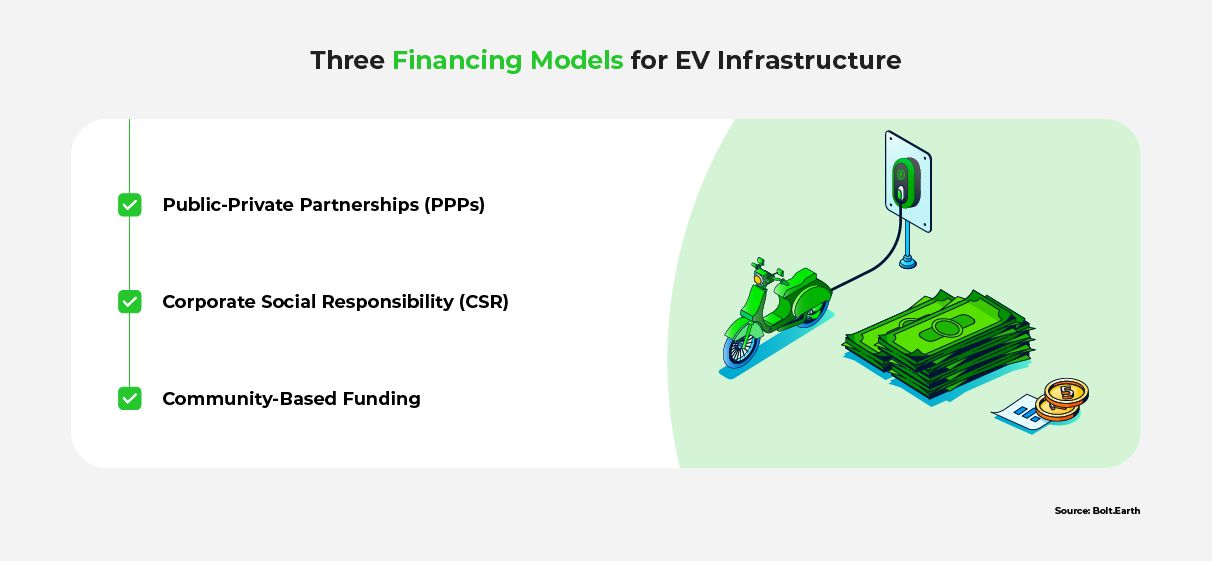
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) foster collaboration between government and private entities to develop and finance EV infrastructure. These partnerships allow for resource pooling, risk-sharing, and shared responsibilities. Such risk-sharing mechanisms make investment more viable for private companies.
To incentivize private sector involvement, funding models like revenue-sharing and performance-based incentives can be implemented. Transparency and fairness are essential to the success and long-term sustainability of these partnerships.
Delhi’s successful PPP implementation is expanding for greater reach. It serves as an example of how collaboration between the government and private entities can drive the growth of EV infrastructure.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Funding
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funding has been mandated by the Companies Act 2013 for companies that meet certain financial thresholds. The act requires eligible companies to allocate at least 2% of their average net profits earned during the previous three financial years on CSR initiatives. The act also provides guidelines on eligible activities, reporting requirements, and monitoring mechanisms for CSR expenses.
CSR funding provides an avenue for companies to invest in environmental causes. In India, the annual CSR funding available exceeds Rs 26,000 crore. Companies can support EV infrastructure financing and development by investing in charging stations as part of their CSR activities, contributing to a greener future.
Establishing charging infrastructure at their offices and their local area can also benefit their employees and the local community.
For companies, CSR spending on EV charging infrastructure offers an opportunity for brand building and enhancing their corporate reputation. Such companies can improve their ESG (Environment, Social, and Governance) score and attract investment from ESG funds.
Additionally, companies that follow sustainable business practices are generally preferred by consumers, employees, investors and the public. A good ESG reputation will benefit companies in multiple ways and help them gain a competitive edge.

Community-Based Funding
Community-based funding involves mobilizing resources from local communities to support the development of EV infrastructure. It encourages grassroots participation and engagement, leading to a stronger commitment to maintaining, utilizing, and promoting the charging infrastructure.
Community funding can complement government and private sector efforts, especially in areas where commercial investments may be limited. This model has been proven successful in various sectors, such as the establishment of India’s robust telecom payphone system. Additionally, recent peer-to-peer (P2P) business models like Airbnb and Uber have achieved global success.
A P2P charging network built by EV enthusiasts who voluntarily contribute to expanding the charging infrastructure map. They can share the availability of their private charging stations with others, helping address gaps in charging infrastructure.
However, community-based funding may face limitations in generating significant capital compared to government or private sector investments as it relies heavily on voluntary contributions and community participation. Scaling up this approach to meet the national demand for charging infrastructure could pose challenges. Nevertheless, it can effectively complement other approaches and fill the gaps in specific regions of India.
Impacts of Indian EV Infrastructure Growth
Implementing innovative EV infrastructure financing approaches in India can have positive economic, environmental, and social impacts, such as job creation, reduced air pollution, and increased energy security. Specific financial relationships can also make a difference.
Economic and Environmental Impact
Public-Private Partnerships, Corporate Social Responsibility initiatives, and community-driven funding for the EV charging infrastructure market in India can contribute to market growth, cost efficiency, revenue generation, employment opportunities, and local economic development.
Public-Private Partnerships
PPPs employ innovative business models that optimize operational costs and enhance the efficiency of charging infrastructure. This results in affordable and accessible charging services for end-users.
Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives
CSR funding establishes charging stations in previously overlooked areas. This not only expands coverage and accessibility for EV owners, but also contributes to economic growth and job creation in these regions.
Community-Driven Funding
Community funding promotes a more inclusive and widespread infrastructure network driven by entrepreneurship. It encourages the development of small businesses and organizations within the community, leading to employment opportunities and local economic development.
Clean-Energy Benefits
EVs increase energy security by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels, as the electricity used for charging can be generated from domestic renewable energy sources. Moreover, EVs have zero tailpipe emissions, leading to improved air quality. This environmental impact generates economic benefits such as reduced healthcare costs from lower levels of respiratory illnesses and related health problems. Thus, the environmental benefits of EV adoption goes hand-in-hand with India’s economic interest, improving quality of life for all across the country.
Economic Windfall
The widespread adoption of EVs can stimulate economic growth and create 50 million direct and indirect job opportunities. The growth of the EV industry can also lead to increased investment, technological advancements, and export opportunities, further boosting the economy. The estimated impact of EV adoption on India’s GDP is Rs 14,42,400 crore boost. This includes the impact from EV component manufacturing, assembly, sales, maintenance, and charging.
India’s Global Leadership in EV Adoption
India has the potential to become a global leader in the EV industry, given its large population and commitment to sustainability. Currently, India is the fifth-largest automobile market in the world, and is on track to be the third-largest by 2030.
By strategically employing public-private partnerships, community-based funding, and CSR initiatives, India can attract investment, foster innovation, and develop an advanced EV ecosystem, leading to a transformative shift toward sustainable mobility and business growth.
The potential for India to become a global leader in EV adoption carries profound benefits and implications and innovative financing approaches could help realize its possibilities.
Promoting the Future Through Collaborative Funding
India’s transition to EVs will help foster economic growth, contribute to climate change mitigation, and improve public health. However, the establishment of a universal and affordable charging infrastructure is essential for India to make this change.
EV infrastructure development is plagued by a lack of funding. To overcome hurdles and expedite India’s transition, India’s communities must seek and instill comprehensive EV infrastructure financing solutions.
Collaborations between government entities and private companies offer a promising approach, leveraging the strengths of both sectors. Innovative financing models, such as strategic partnerships between retail hubs and renewable energy companies, can expedite the development of EV charging infrastructure.
The time is ripe for all stakeholders, including government agencies, investors, and private entities, to come together and develop innovative financing approaches that will shape India’s electric vehicle future. Together, we can ensure a sustainable and prosperous future for India’s transportation sector.
For more information on EV infrastructure financing, please see the FAQ and Resources below.
FAQ
What is public-private partnership financing for EV infrastructure, and how does it work in India?
Public-private partnership (PPP) financing for EV infrastructure involves collaboration between government entities and private companies to develop, finance, and operate charging infrastructure in India. This model allows for the sharing of risks, resources, and expertise between the public and private sectors, accelerating the expansion of EV charging infrastructure networks. It enables the government to address funding constraints in tandem with the private sector.
How can community-based funding models support EV infrastructure development in India?
Community-based funding models involve active participation and financial contributions from local communities for the installation and maintenance of charging stations. This instills a sense of ownership among community members. By harnessing the collective power and enthusiasm of local communities, community-based funding models can supplement government and private sector investments in EV infrastructure development and ensure the establishment of charging infrastructure in areas where traditional financing may be limited.
How can innovative financing approaches for EV infrastructure contribute to India’s sustainability goals?
Innovative financing approaches for EV infrastructure will enable rapid expansion of charging infrastructure. With an increase in charging infrastructure EV users will have universal and affordable access to charging facilities. This will lead to an increase in EV adoption. With more users adopting EVs, India will be able to reduce carbon emissions, improve air quality, and transition to green energy. Thus, innovative financing models support India’s sustainability goals and help to achieve the environmental benefits associated with green energy.
What role can government policies play in facilitating innovative financing approaches for EV infrastructure in India?
Supportive government policies provide a conducive environment for investments in EV infrastructure. A supportive policy framework can include incentives, tax benefits, and subsidies for private sector investments in EV infrastructure. By establishing clear targets and timelines, such as the number of charging stations to be installed the government provides clarity about future investment prospects. Clear and consistent policies provide a sense of stability and reduce uncertainty, attracting investors.
How can stakeholders collaborate to create successful innovative financing approaches for EV infrastructure in India?
Different stakeholders such as government agencies, private companies, and community organizations can collaborate to develop innovative solutions to the charging infrastructure challenges. By pooling their resources, expertise, and perspectives, stakeholders can leverage their respective strengths. Government can formulate a policy framework to encourage public-private partnerships, such as between renewable energy companies and residential communities to set up charging stations. Similarly, private companies and community organizations can work together on CSR projects to establish charging stations.
Resources
CEEW: Financing India’s Transition to EVs
Learn why India needs EV infrastructure financing to boost EV adoption.
IBEF: EV Market in India
Learn about the drivers and obstacles to EV adoption in India.
India Times: How Adequate Finances, Infrastructure Can Provide Fillip to India’s EV Dreams
Learn innovative insights about the needed EV infrastructure financing models to support India’s EV30@30 goals.
The Economic Times: India to See 48k More EV Chargers with Investment of Rs 14,000 Crore in 3-4 Years
Read why the India EV market is in rude health.
India Times: Charging Infrastructure Needs Big Push as EV Adoption Grows in India
Learn about the urgent need for improvements in charging infrastructure.
Inc42: Does India’s Current EV Infrastructure Support The Rising EV Adoption Trend?
Is India’s infrastructure up to the task of facing EV adoption trends?


Mar 05, 2026 • EV Charging Infrastructure
The Hidden Cost of Poor Electrical Design in EV Charging Networks
Read More


